Understanding Keyloggers: The Hidden Threat to Your Cybersecurity

In this article, we will explore the hidden threat of keyloggers and their implications for cybersecurity. We will define what keyloggers are and how they operate, as well as examine their common uses and the risks they pose to individuals and organizations. Additionally, we will identify signs that your device may be infected with a keylogger and provide a practical demonstration of testing a keylogger for educational purposes. Finally, we will outline effective strategies to protect yourself from these cyber threats.
Introduction
Keyloggers have emerged as a significant threat in the realm of cybersecurity, silently capturing keystrokes and compromising personal information without the user's knowledge. These malicious tools can be found in both hardware and software forms, making them versatile and difficult to detect. As we increasingly rely on digital platforms for communication, banking, and personal interactions, understanding the dangers posed by keyloggers is more crucial than ever. In this article, we will explore what keyloggers are, how they function, the potential risks they pose, and the essential measures you can take to protect yourself from these hidden threats.
What are Keyloggers?

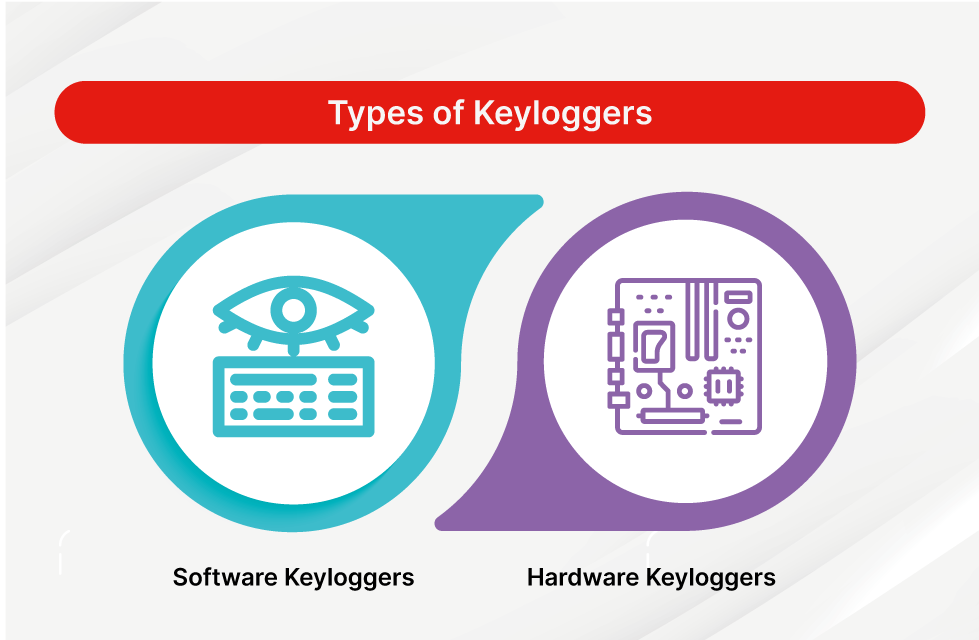
Keyloggers are a type of surveillance tool designed to record every keystroke made by a user on a computer or mobile device. They can be broadly categorized into two main types:
Software Keyloggers: These are applications installed on a device that monitor user activity and capture keystrokes. They often operate in the background without the user's knowledge and can be distributed through malicious downloads, phishing attacks, or bundled with legitimate software. Software keyloggers can capture sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal messages.
Hardware Keyloggers: These are physical devices that are connected between a keyboard and a computer. They can be discreetly installed and do not require any software to be downloaded. Hardware keyloggers are often harder to detect since they do not leave a software footprint, making them particularly dangerous in environments like workplaces or public computers.
Both types of keyloggers can be used for legitimate purposes, such as parental controls or employee monitoring, but they can also be exploited by cybercriminals to steal sensitive information and invade users privacy. Understanding the nature of keyloggers is essential for recognizing their potential threats and taking appropriate measures to protect against them.
How Keyloggers Work
Keyloggers operate by intercepting and recording every keystroke a user makes on their device, often without the user's awareness. Their methods of operation vary depending on whether they are hardware-based or software-based, but their ultimate goal is the same: capturing sensitive information such as passwords, personal messages, or financial details. Here's how each type works:
Software Keyloggers
Software keyloggers are installed directly on a device, typically through malicious downloads, email attachments, or phishing links. Once installed, they run silently in the background, tracking and logging every keystroke. They can also capture screenshots, monitor clipboard activity, or track which applications are being used. Some sophisticated software keyloggers can even bypass security measures, such as antivirus programs, by disguising themselves as legitimate software.
Common methods of installation include:
- Phishing Emails: Attackers trick users into downloading malicious attachments or clicking on harmful links.
- Drive-by Downloads: Visiting a compromised website can automatically install the keylogger without the user's knowledge.
- Malicious Software Bundles: Keyloggers can be hidden within legitimate-looking software, downloaded inadvertently.
Hardware Keyloggers
Hardware keyloggers are physical devices connected to the computer, usually between the keyboard and the computer itself. These devices record all keystrokes as they pass from the keyboard to the system. They require physical access to the target machine for installation, making them harder to deploy on a large scale, but they are much harder to detect because they don't leave any digital traces.
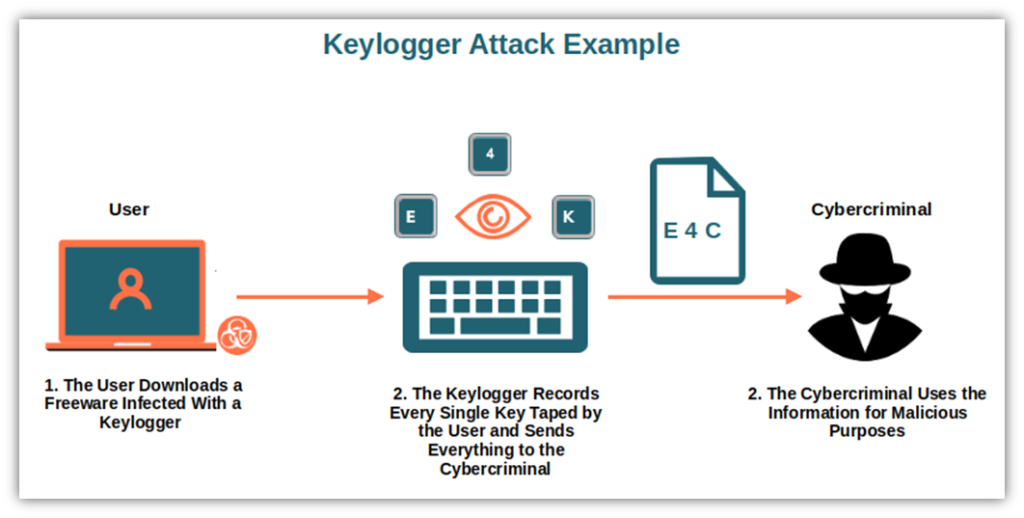
Keyloggers store the captured data locally or transmit it remotely to a designated server controlled by the attacker. In either case, this data can be accessed later for malicious purposes, including identity theft, financial fraud, or corporate espionage.
By understanding how keyloggers work, individuals can better protect themselves against these invasive tools and mitigate the risks they pose.
Common Uses of Keyloggers
Keyloggers can serve both legitimate and malicious purposes, depending on how they are used and by whom. While they are often associated with cybercriminals and hacking activities, keyloggers can also have legal and ethical applications when used responsibly. Below are the most common uses of keyloggers:

Legitimate Uses of Keyloggers
- Parental Monitoring: Parents may use keyloggers to monitor their children's online activity, ensuring that they are not exposed to harmful content or engaging in unsafe communication with strangers.
- Employee Surveillance: Employers might use keyloggers to monitor employee activity on company-owned devices, particularly to track productivity or ensure that sensitive information is not being leaked. However, this must be done in compliance with privacy laws and workplace agreements.
- Law Enforcement: In some cases, law enforcement agencies may use keyloggers to track the activities of suspects during criminal investigations, especially in cases involving cybercrime or terrorism.
Malicious Uses of Keyloggers
- Cybercriminal Activity: One of the most prevalent uses of keyloggers is for illegal activities. Cybercriminals deploy keyloggers to steal sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, bank account details, and other personal data. This information can then be used for identity theft, financial fraud, or sold on the dark web.
- Corporate Espionage: Competitors or rogue insiders may use keyloggers to spy on business communications, capture trade secrets, or gather confidential information. Keyloggers can be discreetly installed on corporate networks, making them powerful tools in espionage.
- Data Theft: Keyloggers are also used to infiltrate systems and steal large amounts of data, including email credentials, encrypted files, or any sensitive material typed by the user.
While keyloggers have some legitimate uses, their potential for misuse makes them a significant cybersecurity threat. Understanding these different uses highlights the importance of safeguarding against keylogger attacks and implementing security measures to protect personal and business information.
Risks and Threats Posed by Keyloggers
Keyloggers present serious risks to individuals, businesses, and organizations due to their ability to capture sensitive data without detection. Whether used by cybercriminals or unethical insiders, the consequences of a keylogger infection can be devastating. Here are the most significant risks and threats they pose:
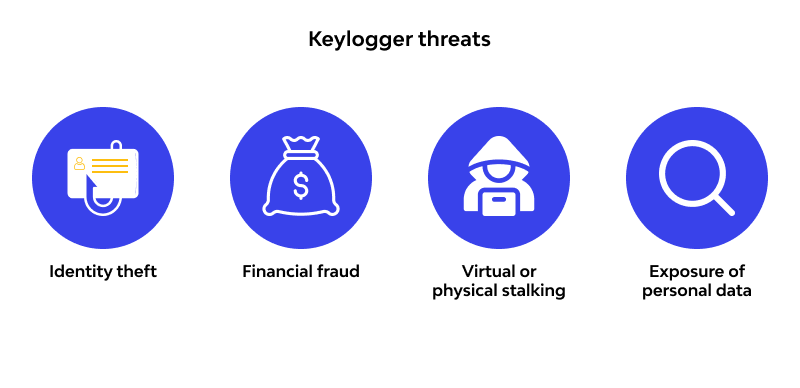
1. Identity Theft
Keyloggers can capture personal information, such as usernames, passwords, social security numbers, and other sensitive details. Cybercriminals can use this data to steal your identity, open fraudulent accounts, or make unauthorized transactions in your name. The consequences of identity theft can take years to resolve and cause severe financial damage.
2. Financial Fraud
By tracking keystrokes, keyloggers can capture online banking credentials, credit card numbers, and payment information. This allows attackers to access financial accounts, transfer money, or make unauthorized purchases, leading to significant financial loss for the victim.
3. Loss of Privacy
A keylogger can monitor everything a user types, including personal conversations, search history, and emails. This invasion of privacy can lead to blackmail, embarrassment, or the leaking of sensitive personal details.
4. Corporate Espionage and Data Breaches
In businesses and organizations, keyloggers can be used to steal confidential information such as trade secrets, intellectual property, or customer data. This can result in costly data breaches, loss of competitive advantage, and significant legal repercussions if sensitive information is leaked or exposed.
5. Compromised Credentials
Once a keylogger captures login credentials, attackers can gain unauthorized access to accounts, including social media, email, and corporate systems. This can lead to further exploitation, including locking users out of their own accounts, posting harmful content, or leveraging access for larger-scale attacks.
6. Widespread Infiltration
A keylogger infection can spread across networks, affecting multiple systems within an organization. Once an attacker has access to one device, they can move laterally through the network, infecting other machines and escalating their control, which can result in large-scale compromises.
7. Reputation Damage
For businesses, the discovery of a keylogger-based breach can result in significant damage to reputation. Customers and partners may lose trust in the company's ability to protect sensitive information, which can lead to lost business, lawsuits, and long-term brand damage.
Given the range of threats posed by keyloggers, it's clear that these tools can be extremely dangerous, both on an individual and organizational level. Protecting against keyloggers is a critical component of maintaining digital security.
Signs That Your Device May Be Infected
Detecting keyloggers can be challenging because they are designed to operate stealthily, often running in the background without obvious signs. However, there are certain indicators that may suggest your device has been compromised by a keylogger. Being aware of these signs can help you take action early to prevent further damage.

1. Unusual System Performance
Keyloggers, especially software-based ones, can slow down your device since they run continuously in the background. If your system starts lagging, becomes unresponsive, or experiences frequent crashes, it could be a sign of malicious software, including keyloggers.
2. Delayed Typing Responses
One of the more noticeable signs of a keylogger infection is a delay between when you type something and when it appears on the screen. This lag may indicate that your keystrokes are being captured and processed by a hidden program before being displayed.
3. Unusual Network Activity
Keyloggers often transmit the captured data to remote servers controlled by attackers. If you notice an unusual spike in network activity, particularly when you're not actively using the internet, it could be a sign that a keylogger is sending your information over the network.
4. Suspicious Programs or Files
If you notice unfamiliar programs or files on your device, they could be linked to a keylogger. Keyloggers can disguise themselves under harmless-looking names, but if you find software or files you don't recognize, it's worth investigating further.
5. Antivirus Warnings
While keyloggers can sometimes evade antivirus software, advanced security programs may still detect them. If your antivirus or security software flags suspicious activity or repeatedly warns you about threats, a keylogger could be the cause.
6. Unexplained Changes in System Settings
Keyloggers and other forms of malware can alter system settings to avoid detection. If you notice unexplained changes to your security settings, firewall rules, or other configurations, it may be a sign that malware, such as a keylogger, is present.
7. Unusual Activity in Accounts
If your online accounts (email, banking, social media) show signs of unusual activity, such as logins from unknown locations or unauthorized transactions, it could mean that a keylogger has stolen your login credentials. Unauthorized access is a serious red flag and should be addressed immediately.
If you suspect that your device is infected with a keylogger based on these signs, it's important to act quickly by running security scans and removing any suspicious software to protect your data from further compromise.
Testing a Keylogger
For educational purposes, testing a keylogger in a controlled environment can be an eye-opening experience. It demonstrates how easily personal data can be captured, even on a seemingly secure system. This test should only be performed in a legal and responsible manner on your own devices or systems that you are authorized to access. The goal is to understand how keyloggers work and the risks they pose, not to misuse the technology.
Disclaimer
Before proceeding, remember that downloading and using keyloggers on devices or networks without consent is illegal and unethical. Always ensure you are complying with local laws and ethical standards.
Step 1: Setting Up a Safe Environment
To test a keylogger safely, set up an isolated test environment:
- Use a Virtual Machine (VM): A VM allows you to run a separate operating system within your computer, ensuring your main system stays safe. Software like VirtualBox or VMware can be used to create a virtual environment.
- Disconnect from the Internet: To prevent accidental data leaks, disconnect the virtual machine from your main network to avoid transmitting any captured data to external sources.
Step 2: Downloading a Keylogger for Testing
There are several keyloggers available online, including open-source keyloggers designed for educational purposes. Look for one that is explicitly labeled for testing or academic use. Examples of open-source keyloggers include:
- PyKeyLog: A simple, open-source keylogger designed by OusCyb3rH4ck for educational purposes.
- Revealer Keylogger: A more advanced tool that can capture keystrokes, though it is typically used for testing.
Ensure you download these tools from reputable sources and scan them for malware before proceeding.
Step 3: Installing the Keylogger
Once you have downloaded the keylogger, install it in your virtual environment. Follow the installation instructions provided by the keylogger software. Most keyloggers will start running in the background once installed, capturing all keystrokes typed into the system.
Step 4: Testing the Keylogger
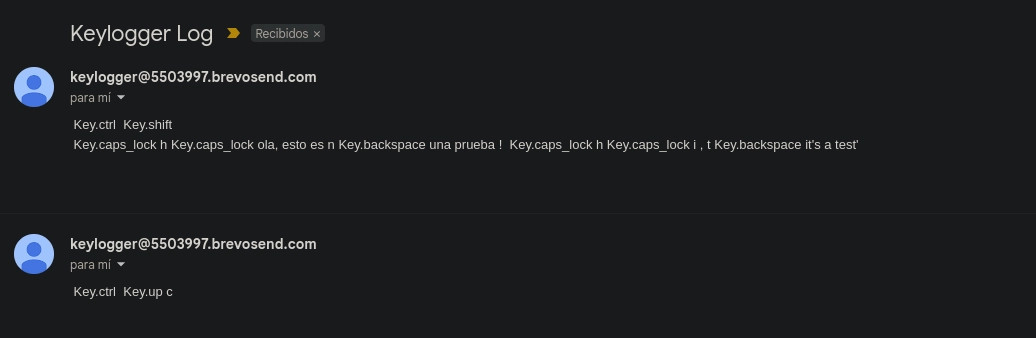
After installation, begin typing in the virtual machine as you normally would—enter text, passwords, or open and use applications. The keylogger will quietly record all this activity. After a period of use, check the logs generated by the keylogger to see what information it has captured.
Step 5: Analyzing the Results
Review the data collected by the keylogger. You'll likely see every keystroke recorded, including personal details, passwords, and other sensitive information. This is a powerful demonstration of how quickly and easily a keylogger can compromise sensitive data.
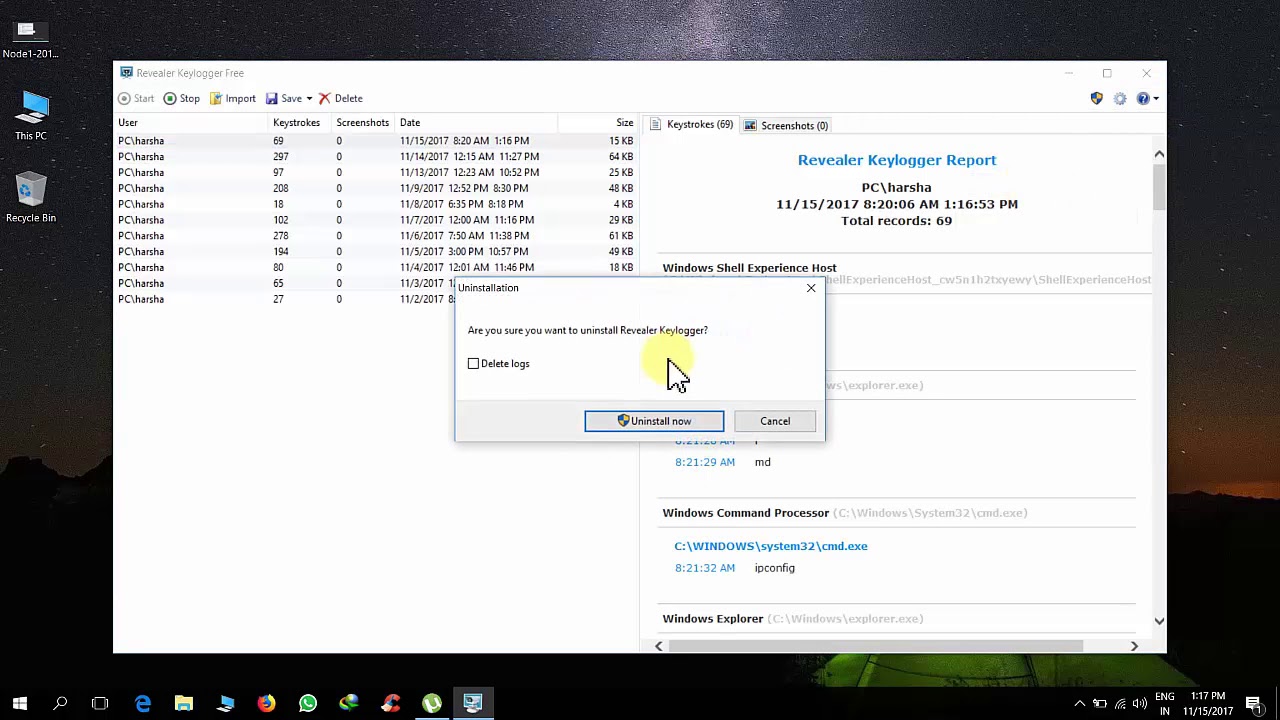
Step 6: Removing the Keylogger
After completing the test, uninstall the keylogger from the virtual environment and restore the VM to its original state by deleting the current session or resetting the machine. This ensures that no harmful software remains on your system.
Conclusion
Testing a keylogger in a controlled setting helps to illustrate how dangerous these tools can be when misused. It highlights the importance of safeguarding against keyloggers and reinforces why cybersecurity measures such as anti-malware software, network monitoring, and safe browsing habits are essential.
How to Protect Yourself from Keyloggers
Given the stealthy nature of keyloggers and the severe risks they pose, taking proactive steps to protect yourself is crucial. Fortunately, there are several effective methods to safeguard your devices and personal information from keylogger infections.

1. Use a Reputable Antivirus Software
One of the best defenses against keyloggers is using a reputable and up-to-date antivirus program. Modern antivirus solutions can detect and remove many types of keyloggers before they cause harm. Regularly update your antivirus software to ensure it has the latest malware definitions to combat new threats.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts. Even if a keylogger captures your password, attackers would still need access to the second authentication factor (such as a mobile phone or email code) to log in. Always enable 2FA on sensitive accounts like banking, email, and social media.
3. Install a Firewall
A firewall monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and can help prevent keyloggers from transmitting your data to an external server. Use both software firewalls (built into most operating systems) and hardware firewalls (included in many routers) to provide an additional line of defense.
4. Keep Your Software and Operating System Updated
Outdated software often contains security vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit to install keyloggers. Regularly update your operating system, browsers, and other critical applications to patch security holes. Enabling automatic updates can ensure you stay protected without having to manually update.
5. Use Anti-Keylogger Software
Specialized anti-keylogger software is designed specifically to detect and prevent keyloggers from operating. These programs offer real-time protection and can block keyloggers from logging keystrokes. Some popular anti-keylogger tools include Zemana AntiLogger and SpyShelter.
6. Be Cautious with Downloads and Links
Avoid downloading software from untrusted or unknown sources, as malicious downloads are a common way keyloggers spread. Similarly, be wary of clicking on links in unsolicited emails or suspicious websites. Always verify the legitimacy of the source before downloading any files.
7. Use a Virtual Keyboard for Sensitive Information
When entering highly sensitive information, such as passwords or banking details, consider using a virtual keyboard. Many online banking platforms offer this feature. Virtual keyboards are more difficult for keyloggers to capture because they record physical keystrokes, not mouse clicks.
8. Monitor Network Activity
Keep an eye on your device's network activity, as keyloggers often transmit the captured data to remote servers. If you notice unusual outgoing traffic when you are not actively using the internet, it could be a sign of a keylogger or other malware. Network monitoring tools can help identify these anomalies.
9. Regularly Scan Your Device
Perform regular scans with security software to detect hidden keyloggers or other malware. Even if your system seems to be functioning normally, periodic scans can help uncover and remove threats before they cause serious damage.
10. Be Wary of Public Computers
Avoid entering sensitive information (such as passwords or credit card details) on public or shared computers, as these machines could be infected with keyloggers. If you must use a public computer, ensure that you log out of all accounts and avoid entering personal information whenever possible.
Conclusion
Protecting yourself from keyloggers requires a combination of good cybersecurity practices, such as using strong security software, staying vigilant about downloads and network activity, and enabling two-factor authentication. By taking these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to keyloggers and other types of cyber threats.
Conclusion
Keyloggers represent a serious and often invisible threat to both individual users and organizations. Their ability to silently capture sensitive data such as passwords, personal messages, and financial information makes them a powerful tool for cybercriminals. Throughout this article, we've explored what keyloggers are, how they function, and the significant risks they pose. We also conducted a practical test of a keylogger to understand its potential impact firsthand and reviewed essential strategies to protect against them.
The key to defending yourself from keyloggers lies in staying vigilant. By implementing robust cybersecurity practices—such as using reputable antivirus software, enabling two-factor authentication, keeping your systems updated, and being cautious with downloads—you can significantly reduce the likelihood of a keylogger infiltrating your device.
Understanding the dangers posed by keyloggers is a critical step toward ensuring your digital safety. The more proactive you are in protecting yourself, the less likely you are to become a victim of these hidden threats.
