Is Python the Best Programming Language for Ethical Hacking in 2025?

Whether you're a seasoned penetration tester, a blue team analyst, or just stepping into the world of ethical hacking, one question always pops up:
"What's the best programming language to learn for cybersecurity?"
There are dozens of strong contenders—C, Go, Rust, Bash, even PowerShell—but one language continues to dominate hacker toolkits, courses, and GitHub repos alike: Python.
In this article, we'll explore why Python has become the go-to language for ethical hackers and cybersecurity professionals. We'll break down its strengths, where it shines, where it struggles, how it compares to other languages in the field, and ultimately try to answer the big question:
Is Python still the best programming language for ethical hacking in 2025?
Let's get into it.
1. Introduction: Python & the Hacker's Choice 🐍💻
When it comes to ethical hacking, Python is everywhere. From quick one-liners to fully fledged attack frameworks, it has cemented its place as a hacker's favorite. But why?
It's not just hype — Python brings a mix of power, flexibility, and simplicity that makes it ideal for security professionals at any level. Whether you're automating a reconnaissance script, crafting a custom exploit, or analyzing log files from a breach, Python lets you move fast and focus on the what, not get lost in the how.
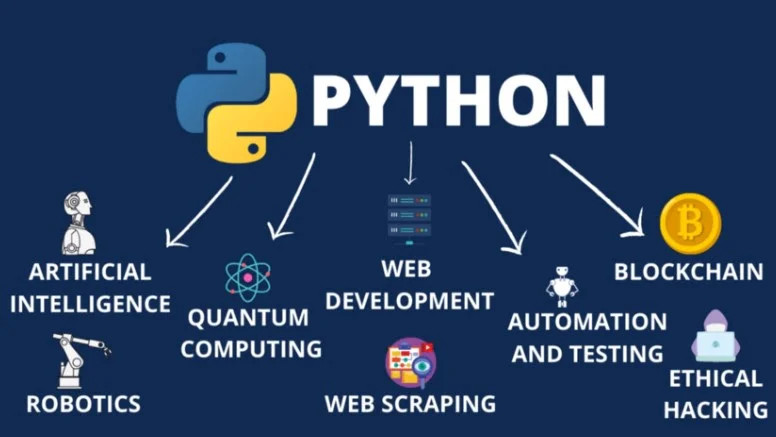
Here's why it's often called "the hacker's Swiss army knife":
-
🧠 Easy to learn, hard to outgrow: Python's readable syntax means less time fighting the language, more time breaking systems (ethically, of course).
-
🔌 Massive library ecosystem: From packet crafting to web scraping, chances are there's already a module that does exactly what you need.
-
🛠️ Toolchain integration: Python plays well with Linux, APIs, databases, and pretty much anything else you'd encounter during an engagement.
-
🌐 Community-driven: Thousands of open-source tools and active contributors make it easy to find inspiration or code to repurpose.
In the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, where time matters and tools evolve constantly, Python gives ethical hackers the agility and creative freedom they need.
So, is Python just a popular language, or is it actually the best for ethical hacking?
Let's take a deeper look.
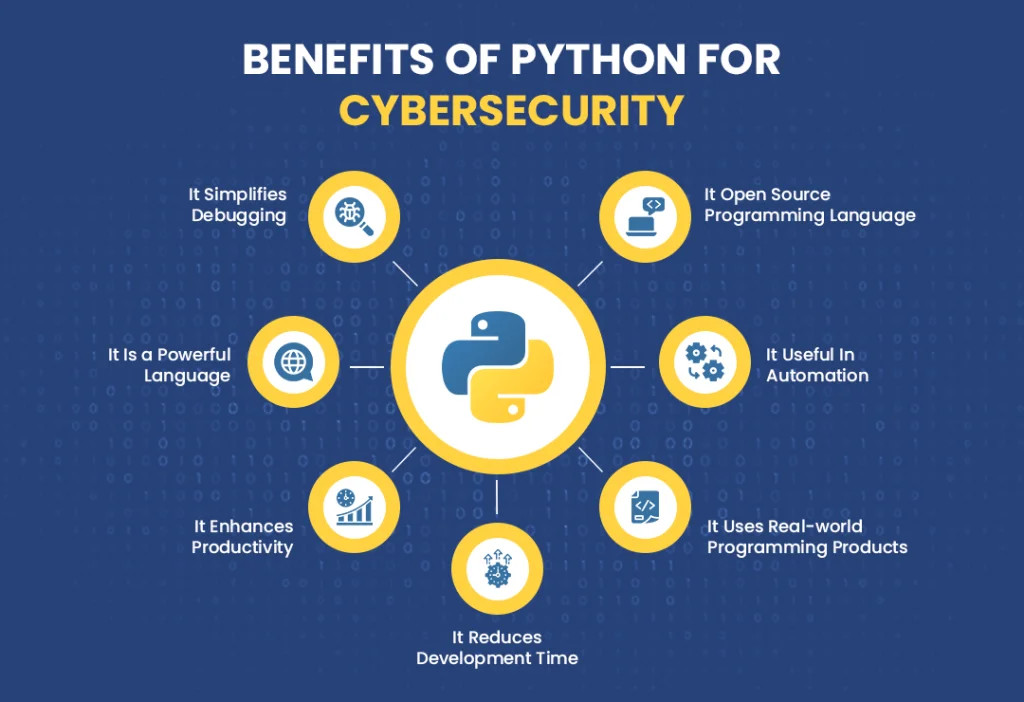
2. Why Python Fits Like a Glove in Cybersecurity 🧤🔐
In ethical hacking, success often depends on how fast you can build, adapt, and deploy tools in the field. This is where Python really shines — not just as a language, but as a cybersecurity enabler. Here's why it fits the needs of both rookies and pros like a custom-made glove:
🧵 Simple Syntax = Fast Scripting
Python's clean, human-readable syntax makes it incredibly fast to write and understand. Need a script to scan a subnet? Automate a brute-force login? Scrape data from a web app? You can often do it in just a few lines of code, even during a live engagement.
Compare this to C or Java, where even a basic task can feel like writing a novel. Python removes that friction — and in cybersecurity, speed matters.
⚡ Perfect for Rapid Prototyping
New exploit idea? Need a quick proof of concept? With Python, you can go from concept to code in minutes. This is especially important during CTFs, red team engagements, or bug bounty hunts, where reacting fast gives you the upper hand.
Plus, with Python's dynamic typing and lack of compilation, tweaking code on the fly is easy — no compile-run-debug cycles slowing you down.
🔗 High-Level, Yet Capable of Low-Level Work
Python is high-level enough to feel effortless, but also gives access to low-level operations when needed. You can:
-
Craft raw packets with Scapy
-
Interact with the OS via os and subprocess
-
Hook into sockets and manipulate protocols
-
Decode or encode in almost any format (Base64, Hex, JWT, etc.)
It's like having Bash and C merged, with none of the headaches.
🧰 Multitool Mindset = One Language, Many Roles
Python works across the entire cybersecurity spectrum:
-
✅ Reconnaissance (web scraping, subdomain enumeration)
-
✅ Exploitation (custom payloads, CVE scripts)
-
✅ Post-exploitation (persistence, lateral movement)
-
✅ Defense (log parsing, alert automation, threat intel)
Few languages offer that level of versatility without switching ecosystems.
In short, Python doesn't just "work" for ethical hacking — it adapts, evolves, and empowers.
It's not just a tool; it's the hacker's mindset, written in code.
3. Essential Python Libraries and Tools for Ethical Hacking 🧰🐍
One of Python's greatest strengths in the cybersecurity field is its massive library ecosystem. You don't have to reinvent the wheel — chances are, there's already a Python module that does exactly what you need... or at least gets you 90% of the way there.
Here's a curated list of must-know Python libraries and tools used by ethical hackers, red teamers, and security researchers in 2025:
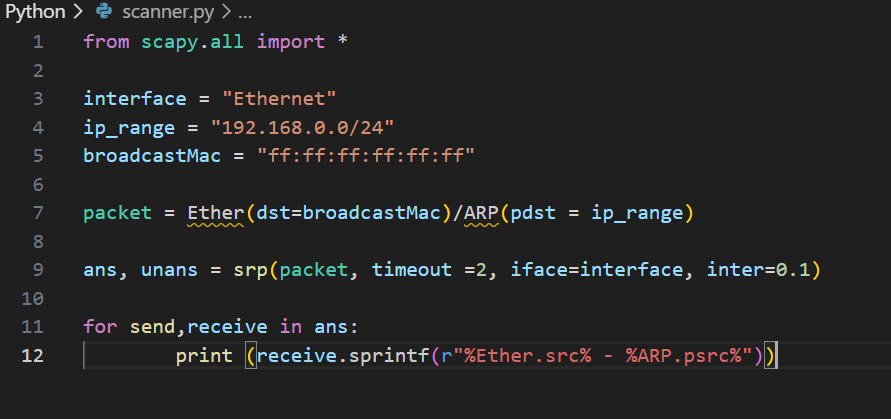
🧪 Scapy
The king of packet crafting and network analysis.
With Scapy, you can build custom packets from scratch, send them across the network, and sniff the responses — perfect for testing firewall rules, spoofing traffic, or crafting protocol-specific attacks.
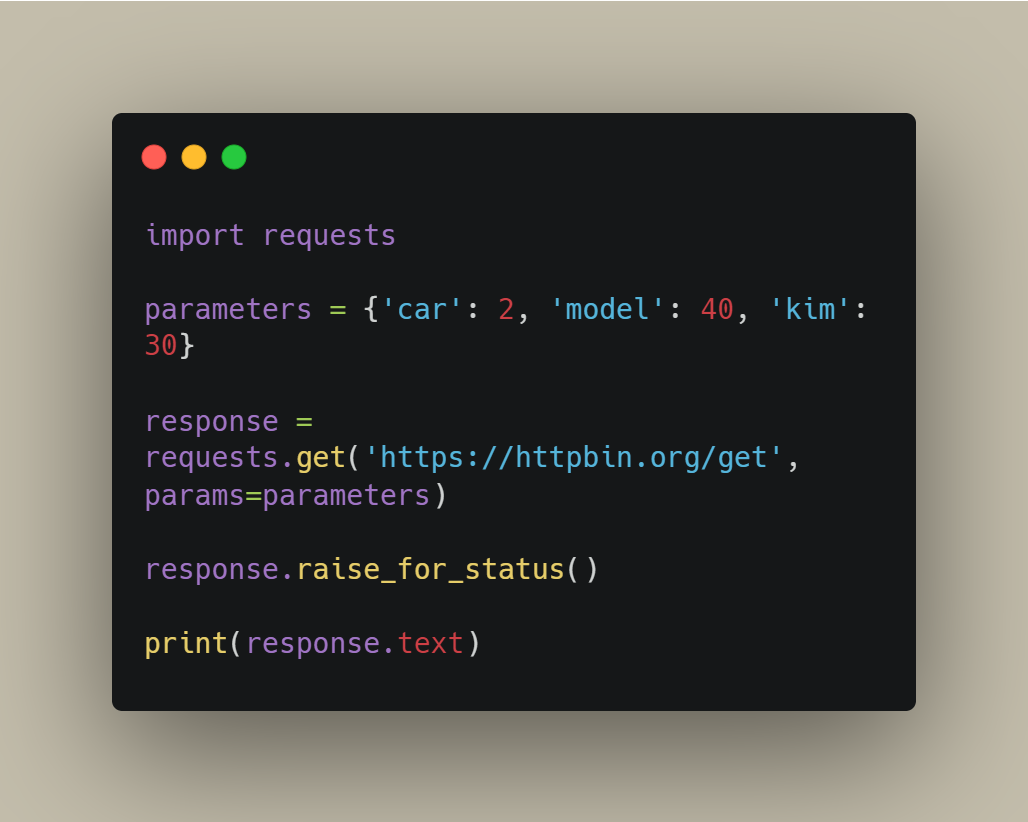
🌐 Requests
Web requests made simple.
Whether you're automating login attempts, scraping headers, or building your own scanner, requests gives you full control over HTTP interactions — with elegance.
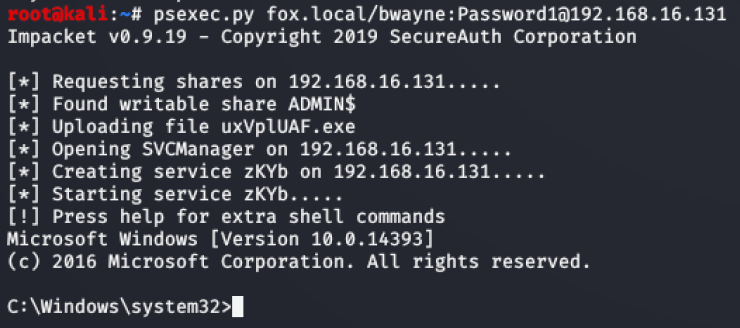
🔓 Impacket
A collection of Python classes for working with network protocols.
Especially powerful for red teamers, Impacket supports SMB, RDP, LDAP, and more — and enables techniques like Pass-the-Hash, Kerberos abuse, and command execution over remote protocols.
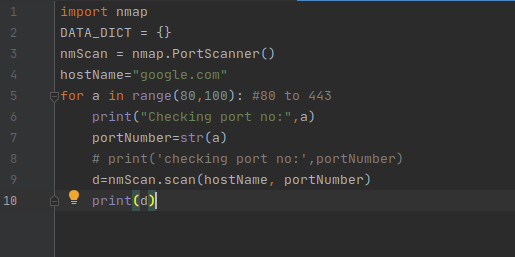
📡 Nmap (via python-nmap)
Integrate the world's most famous port scanner with your own scripts.
You can run scans, parse results, and even automate pivoting logic inside your Python code.
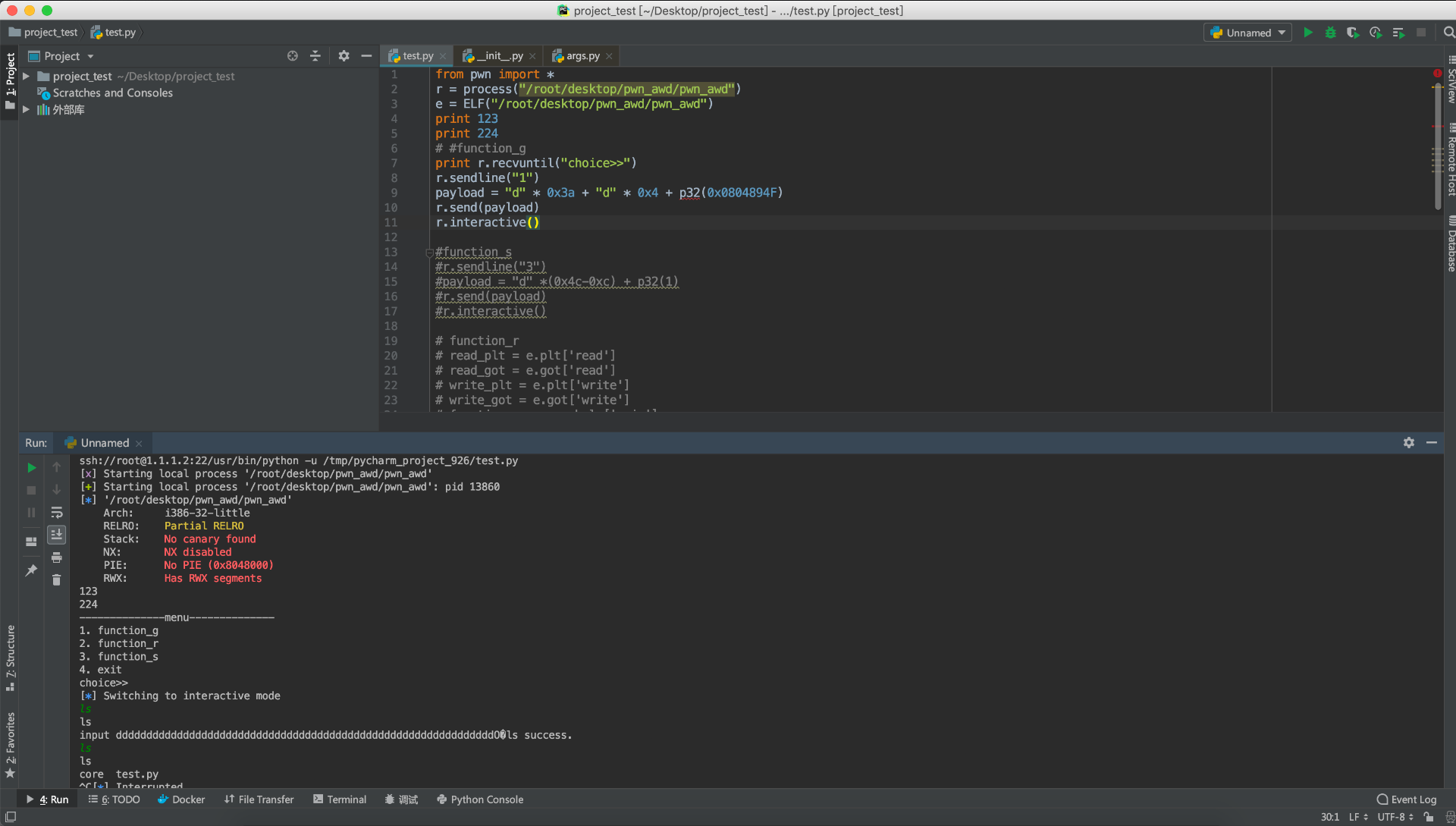
🐚 Pwntools
Designed for CTFs and binary exploitation.
This is your go-to library for pwn challenges, exploit development, and interacting with remote services. It abstracts away complex socket logic and makes payload crafting feel like magic.
🔐 Paramiko
SSH in pure Python.
Use it to automate SSH access, run commands remotely, or even build your own botnet-style control system (ethically, of course 👀).

📎 Bonus: Other Libraries You Should Know
-
BeautifulSoup / lxml – Web scraping and HTML parsing
-
Socket – Lower-level networking control
-
OS / Subprocess – Shell command execution
-
Cryptography / hashlib – Hashing, encoding, encryption tools
-
Shodan API – Integrate real-world data into recon tools
These libraries are battle-tested in real-world engagements, CTFs, and security research. Knowing how to use them gives you a huge edge, whether you're building custom tooling or automating your workflow.
Learn them. Master them. Bend them to your will 😈
4. Python for Offensive Security: Red Teaming & Exploits 🔓💥
When it comes to offensive security, Python is much more than just a programming language — it's a weapon of choice for red teamers, penetration testers, and exploit developers. Python's ability to rapidly prototype and automate attacks makes it an essential tool in the offensive security toolkit.
Let's break down how Python is used in red teaming, exploitation, and the automation of offensive tasks:
💣 Crafting Exploits
Python's power to quickly create custom exploits is unmatched. Whether it's for buffer overflows, SQL injections, or web vulnerabilities, Python simplifies exploit development, allowing hackers to move fast and hit hard.
-
PwnTools is a prime example, widely used in Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions and bug bounty programs. It provides easy access to network protocols and makes crafting payloads for exploits feel seamless.
-
Using Python, you can automate tasks like buffer overflow exploitation or even create custom web shells for post-exploitation.
Example of exploiting a buffer overflow vulnerability using Python:
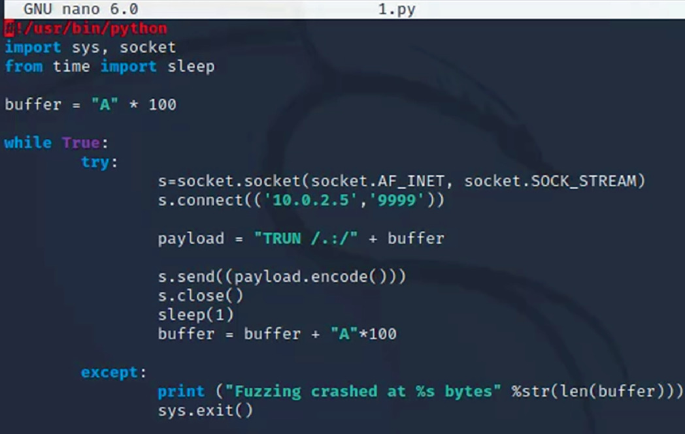
🕹️ Automating Attacks
Python excels at automating tasks, and in the offensive security world, automation is key. Whether it's a brute force attack, web application scanning, or even automating the post-exploitation phase, Python allows you to set up and execute these tasks with just a few lines of code.
Examples include:
-
Brute-forcing SSH or RDP credentials using libraries like paramiko and pexpect
-
Web scraping with requests and beautifulsoup to automate the discovery of exposed services or admin panels.
Automating the attack process means less time spent on repetitive tasks and more time spent on discovering vulnerabilities.
🛠️ Building Custom Tools
Python empowers ethical hackers to build their own penetration testing tools. You don't always need pre-built frameworks; sometimes, you just need a custom solution that fits your needs. Python allows you to build tools for:
-
Reconnaissance (automated scanning, port scanning, vulnerability enumeration)
-
Exploitation (custom payload generation, remote command execution)
-
Post-exploitation (pivoting, lateral movement, data exfiltration)
Popular frameworks like Metasploit use Python for scripting and exploiting, while tools like Empire (a PowerShell-based framework) also make use of Python for scripting custom tasks.
🕵️♂️ Reconnaissance and Information Gathering
Gathering intel is an essential part of offensive security, and Python is a go-to language for automating recon. Python can interact with various APIs and scrape data to help identify vulnerable systems, services, and users.
-
Shodan API allows you to search for vulnerable internet-connected devices and exposed services, integrating it with Python to automate scans.
-
TheHarvester and custom scripts can be used for OSINT (open-source intelligence) gathering, gathering emails, domains, and other key data points.
Example of using the Shodan API with Python:
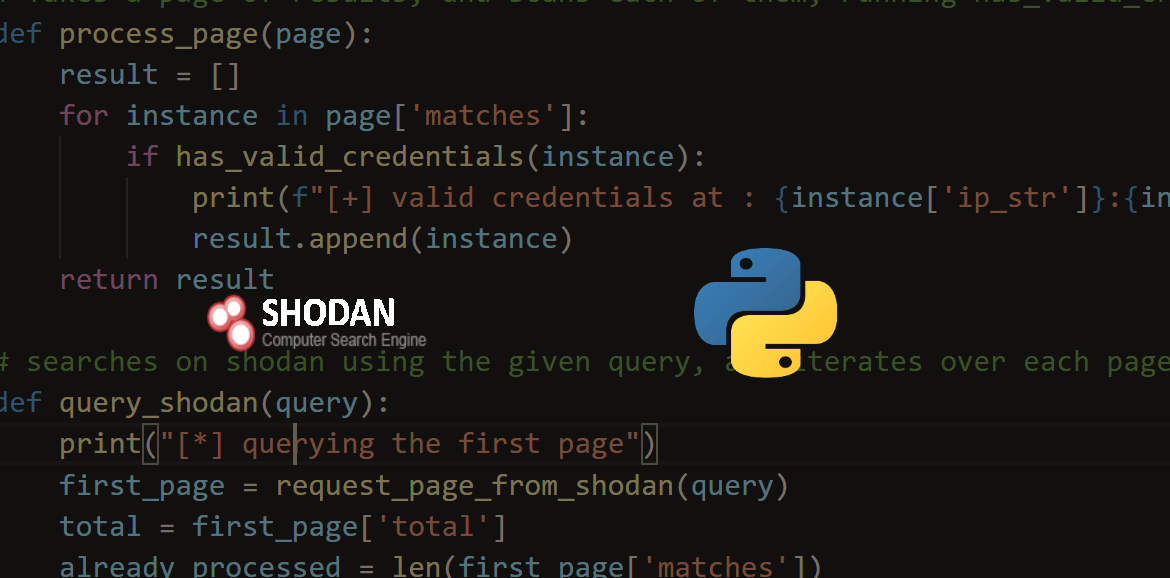
💼 Exploitation Frameworks
Python is also integral to post-exploitation frameworks. For example:
-
Pupy: A powerful multi-platform remote administration tool often used by red teamers for persistent access, written in Python.
-
Covenant: A post-exploitation framework also built using Python, allowing attackers to manage compromised systems and execute post-exploitation actions.
These tools allow red teamers to automate persistence, lateral movement, and data exfiltration, all while staying within a single language ecosystem.
🛡️ Evasion Techniques: Using PyArmor
Python also plays a key role in evading detection, especially when antivirus (AV) and Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) systems are in play. Since Python is interpreted and easy to detect, it can sometimes be blocked by security systems.
This is where PyArmor comes in. PyArmor is a Python obfuscation tool that helps protect Python scripts from being reverse-engineered and avoiding detection. It encrypts and obfuscates your Python code, making it much harder for security tools to detect and analyze your scripts.
Here's how PyArmor helps:
-
Obfuscates Python bytecode: Making it harder for attackers or defenders to read or reverse engineer.
-
Encrypts Python scripts: Even if someone gains access to your script, they won't easily know what it does.
-
Prevents code analysis: By making the code hard to decompile or debug, PyArmor significantly increases the complexity of detecting malicious Python payloads.
Example of using PyArmor to protect a script:
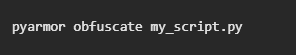
Using tools like PyArmor ensures that your payloads, shellcodes, and custom tools remain undetected during engagements, giving you a stealth advantage.
Python is a critical part of the offensive security toolkit. Its ability to automate, prototype, and evade detection makes it an invaluable asset for red teamers and pen testers in the fight against cyber threats.
5. Python for Defensive Security: Monitoring & Automation 🧑💻🔐

While Python is widely recognized in the offensive security world, it's also an absolute game-changer for defenders. Whether you're a blue teamer or working in incident response (IR), Python's simplicity, flexibility, and automation power can significantly boost your defensive security efforts. Here's how Python helps in monitoring, incident detection, and automation:
🔍 Automating Log Analysis
One of the biggest challenges in defensive security is sifting through logs to find signs of malicious activity. Python shines in this area, as it can be used to automate log parsing and real-time alerting.
By using libraries like loguru, json, and regex, defenders can create scripts that automatically analyze system logs, application logs, or security logs to detect anomalies that might indicate an attack.
🕵️♀️ Threat Intelligence Automation
Python can be used to integrate threat intelligence feeds into your security infrastructure. By using libraries like requests to interact with APIs, defenders can fetch information about new vulnerabilities, IOCs (Indicators of Compromise), or zero-day exploits and automatically update firewalls, IDS, or SIEM systems.
For example, integrating the AlienVault OTX (Open Threat Exchange) feed into your system using Python.
⚙️ Automating Incident Response (IR)
When an incident occurs, speed is critical. Python can be used to automate incident response actions such as isolating compromised systems, collecting evidence, or blocking malicious IPs. Tools like psutil or subprocess can interact with the system to execute immediate defensive actions.
For example, you can write a Python script to block a malicious IP on your firewal.l
This allows for automated containment of threats during an ongoing attack, limiting the damage while you investigate further.
🛡️ Building Security Monitoring Tools
Python is great for building custom security monitoring tools that can alert you to potential threats in real-time. Whether it's monitoring for unusual network traffic, failed login attempts, or unauthorized file changes, Python can be used to track key events in the environment and notify you when suspicious activity occurs.
For example, a script that monitors a specific directory for unauthorized changes.
🖥️ Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Python is often used in EDR solutions, helping to monitor and react to malicious activities on endpoints. By integrating with antivirus, firewalls, and SIEMs, Python can automate the process of collecting, analyzing, and responding to endpoint alerts.
For example, using Python to automate file integrity checking on endpoints.
🌐 Network Traffic Monitoring
Python can also be used for network traffic analysis and intrusion detection. Libraries like scapy and dpkt allow defenders to build custom scripts to sniff traffic, analyze packets, and detect suspicious behavior (e.g., DDoS attempts, port scanning).
For example, using Python to detect ICMP flood (ping flood) attacks.
💻 Building a SOC with Python
Python's ability to automate tasks and integrate with multiple security systems makes it perfect for building Security Operation Centers (SOC) or SIEM-like platforms. You can create your own custom dashboard for monitoring alerts, logs, and events in real time, making it easier to respond to threats faster.
In summary, Python isn't just for attackers. Its simplicity and versatility make it an excellent choice for defensive security tasks. By automating key defensive actions, building custom monitoring solutions, and integrating threat intelligence, Python empowers defenders to act quickly and efficiently when every second counts.
6. Python vs. Other Languages in Ethical Hacking: Why Python Dominates 🐍💪
While Python is widely regarded as the best programming language for hacking and cybersecurity, there are other languages that also hold their ground. However, when it comes to simplicity, flexibility, and speed of development, Python tends to outshine the competition. In this section, we'll compare Python with other popular languages like C/C++, JavaScript, and Go, and discuss why Python remains a go-to choice for ethical hackers.
🐍 Python vs. C/C++: The Battle of Low-Level vs. High-Level
-
C/C++ is often the preferred language for low-level exploits and system-level attacks because of its ability to interact with hardware directly. It's also the go-to for creating fast and efficient exploits or writing custom rootkits. However, C and C++ come with a steeper learning curve, and memory management is manual, making it more prone to errors.
-
On the other hand, Python is higher-level, meaning it abstracts away complex operations like memory management, which makes it more user-friendly and faster to develop with. Additionally, Python has a huge ecosystem of libraries that can help you get started with ethical hacking tasks without needing to go into deep system-level programming.

When to choose Python over C/C++:
-
Rapid prototyping of tools and scripts.
-
Tasks that require heavy use of existing libraries (e.g., networking, web scraping, automation).
-
Focusing on the attack surface rather than intricate system-level vulnerabilities.
🌐 Python vs. JavaScript: The Web Penetration Showdown
Both Python and JavaScript are incredibly powerful when it comes to web security, but they each have their strengths:
-
JavaScript is essential for client-side attacks like XSS (Cross-Site Scripting), DOM-based attacks, or session hijacking. It's also the language of choice for exploiting web app vulnerabilities and interacting with the browser directly.
-
Python, however, shines when it comes to web scraping, server-side exploitation, and automated tasks like SQL injection testing or fuzzing. With libraries like requests, beautifulsoup, and Selenium, Python makes web penetration testing easier and more scalable.
When to choose Python over JavaScript:
-
When you need to perform automated security testing.
-
For backend exploitation or interacting with web APIs.
-
Building command-line tools or network-based attacks.
🚀 Python vs. Go: The Speed Trade-Off
Go (Golang) has gained significant popularity in the cybersecurity world due to its performance and concurrency support. It's commonly used for building high-performance network scanners, distributed systems, and security tools that need to handle large-scale operations.
-
Go is faster than Python, as it is compiled into machine code, which makes it suitable for tasks where speed is a priority (e.g., port scanning, DDoS attacks, or packet analysis).
-
Python, while not as fast as Go, offers much more in terms of ease of development. You can quickly write and test your ideas without worrying about optimization right off the bat. Python also excels at integrating with existing security tools and libraries.
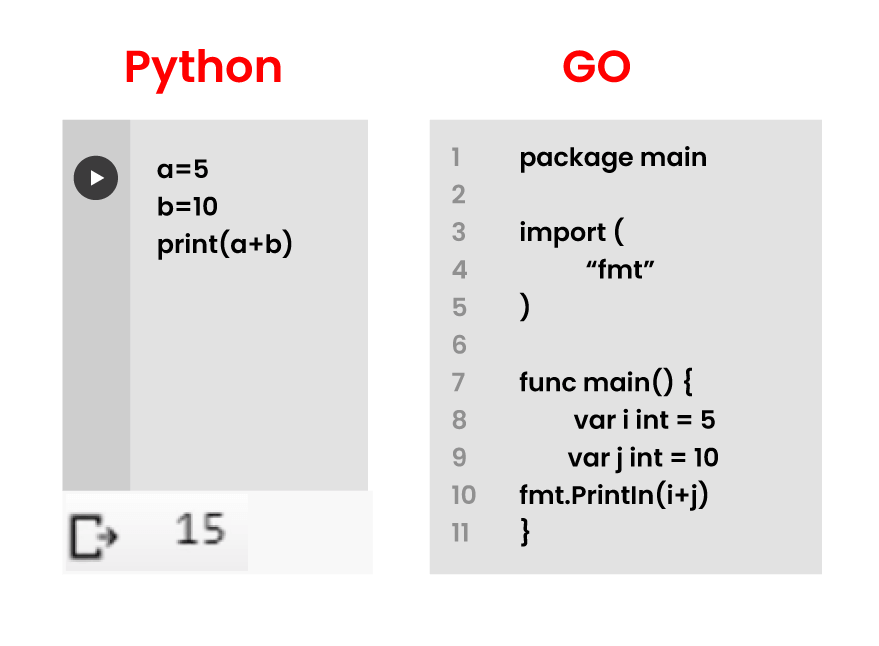
When to choose Python over Go:
-
When you need to rapidly prototype a security tool.
-
When you prefer a language with a large community and a wealth of existing libraries.
-
If the task is more about automation and scripting rather than raw performance.
🧑💻 Python's Ecosystem: A Major Advantage in Ethical Hacking
One of the strongest reasons Python dominates the cybersecurity space is its vast ecosystem of libraries, frameworks, and tools that are designed for security research, penetration testing, and vulnerability exploitation. Unlike C, C++, or Go, Python offers pre-built solutions that let you get straight to the attack or defense without needing to write everything from scratch.

Some key advantages of Python's ecosystem:
-
Penetration testing tools like Metasploit, Impacket, and Pwntools are either written in Python or have Python bindings.
-
For network traffic analysis, Scapy allows you to craft and manipulate packets with ease, while socket and requests help with low-level networking tasks.
-
Libraries like BeautifulSoup and Selenium make web exploitation and scraping a breeze, with very little overhead.
⚖️ Python's Speed of Development vs. Other Languages
The most important factor when choosing a language for ethical hacking or cybersecurity research is speed of development. Time is always of the essence when performing penetration tests or investigating vulnerabilities. Python's simplicity allows you to quickly develop scripts, test payloads, and integrate with existing security tools.
In contrast, languages like C/C++ or Go often require more time to write and debug, making them less suited for fast-paced tasks like bug bounty hunting or CTF competitions.
💡 Conclusion: Why Python Reigns Supreme in Ethical Hacking 👑
While other languages like C/C++, JavaScript, and Go each have their place in the cybersecurity world, Python's simplicity, speed of development, and vast ecosystem of libraries and tools make it the go-to language for most ethical hackers.
-
If you're working on rapid exploitation, web testing, or automating security tasks, Python remains your best bet.
-
If your focus is on low-level system exploitation or network performance, languages like C/C++ or Go might be a better fit.
In the end, Python's ease of use and maturity in the cybersecurity space make it the best choice for beginners and seasoned professionals alike. It allows you to get things done faster, leverage existing tools, and focus on what matters: staying one step ahead of cybercriminals.
7. How to Learn Python for Ethical Hacking: A Roadmap for Success 🧑💻💡
Learning Python is an essential step for anyone looking to break into the world of ethical hacking and cybersecurity. Python's simplicity, flexibility, and power make it an invaluable tool for automating attacks, creating custom exploits, and securing systems. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned security professional, understanding the right approach to learning Python for hacking is key to improving your skills.
Here's a comprehensive roadmap to help you learn Python for ethical hacking and take your skills to the next level.
🏁 1. Start with the Basics: Learn Python Fundamentals
Before diving into ethical hacking and cybersecurity, it's important to master the basic Python concepts. This will give you a solid foundation to build more complex scripts and tools. Here's what you should focus on:
-
Variables and data types (strings, integers, lists, etc.)
-
Control flow (if/else statements, loops)
-
Functions (how to write and use functions in Python)
-
Modules and libraries (importing and using external libraries)
-
Exception handling (try/except to deal with errors)
Recommended resources:
-
Codecademy Python Course
-
Automate the Boring Stuff with Python (great for automation tasks)
-
Python.org Documentation for official references
Once you understand these core concepts, you'll be ready to start applying Python to security-specific tasks.
🕵️♂️ 2. Dive into Ethical Hacking Basics
Now that you're familiar with the fundamentals, it's time to explore the specific applications of Python in ethical hacking. You should focus on:
-
Networking and sockets: Understanding how Python can interact with networks is crucial for tasks like port scanning, packet sniffing, and brute force attacks.
-
Web security: Learn how Python can be used to exploit web vulnerabilities (e.g., SQL injection, XSS) using libraries like requests, BeautifulSoup, and Selenium.
-
System exploitation: Learn how Python can interact with the file system, memory, and network services for privilege escalation and post-exploitation tasks.
Practical exercises:
-
Try writing a basic port scanner using Python's socket module.
-
Automate a SQL injection test using Python and requests.
-
Write a Python script to automate password cracking on a local machine.
💻 3. Learn Python for Penetration Testing & Exploitation Tools
Next, focus on understanding how Python is used in popular penetration testing frameworks and exploitation tools. Learn how to customize these tools or even build your own from scratch:
-
Metasploit: A widely-used framework for penetration testing. Learn how Python is used to script custom exploits and payloads.
-
Pwntools: A powerful Python library that simplifies the process of CTF challenges, binary exploitation, and creating custom exploits.
-
Scapy: A Python tool used for creating and analyzing network packets. Learn how to use it for network scanning, packet injection, and DDoS attacks.
Practice:
-
Follow along with CTF challenges to apply Python in practical exploitation.
-
Write custom exploits or payloads using Pwntools and Scapy.
🛡️ 4. Automate Security Tasks: Build Your Own Security Tools
Once you've gained some hands-on experience with penetration testing, the next step is automation. Python is perfect for creating custom security tools that can save you time and improve efficiency during vulnerability assessments and incident response:
-
Build a simple web scraper to scan a website for common vulnerabilities (e.g., exposed login panels or outdated software).
-
Write a brute force script to test the strength of passwords on various services.
-
Automate log analysis to detect suspicious activity on a server or network.
By automating routine tasks, you'll increase your efficiency and be able to focus on more important aspects of the job.
Example project:
-
Build a file integrity checker that compares file hashes to detect unauthorized changes.
📚 5. Learn Offensive & Defensive Security Techniques
As you become more comfortable with Python, it's essential to balance both offensive and defensive security techniques:
-
Offensive Security: Write scripts for exploitation (buffer overflows, RCE) and recon (scanning, fingerprinting, enumeration).
-
Defensive Security: Use Python for log monitoring, incident response automation, and network traffic analysis.
-
Learn how Python can be used to develop custom defense mechanisms like intrusion detection systems (IDS) or firewall rules.
Recommended tools to explore:
-
Wapiti, a Python-based web application vulnerability scanner.
-
OSQuery, a tool to query operating system data (great for incident response).
🏆 6. Contribute to Open-Source Projects & Practice CTFs
A great way to solidify your learning and improve your Python skills for ethical hacking is by contributing to open-source security projects. Many tools and libraries in the cybersecurity space are open-source, and getting involved can help you understand how professionals write secure, efficient, and scalable Python code.
Additionally, Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions are an excellent way to practice your skills in a competitive and collaborative environment. Many CTF challenges involve using Python for tasks like web exploitation, reverse engineering, and network traffic analysis.
Recommended CTF platforms:
-
Hack The Box (HTB)
-
TryHackMe
-
CTFtime (to find ongoing CTFs)
🎓 7. Keep Learning and Stay Updated
The world of ethical hacking and cybersecurity is always evolving, and so is Python's role within it. Stay updated with the latest security trends, vulnerabilities, and Python libraries by reading blogs, attending conferences, and participating in security communities.
-
Follow cybersecurity blogs like Security Week, Krebs on Security, or PentesterLab for the latest insights.
-
Join security forums or Reddit threads like r/ethicalhacking and r/cybersecurity to learn from experts.
-
Contribute to GitHub repositories or Python forums to continue growing your expertise.
💡 Final Thoughts: Your Python Journey in Ethical Hacking 🚀
Learning Python for ethical hacking is not a sprint but a marathon. Whether you're looking to become a penetration tester, red teamer, blue teamer, or security researcher, Python will be your most powerful ally. By building your foundation with Python fundamentals, experimenting with security tools, and automating tasks, you'll be well on your way to mastering the language and excelling in the world of cybersecurity.
Remember, the key is to keep practicing, keep building, and keep challenging yourself with real-world scenarios. Whether you're writing your own tools or contributing to open-source security projects, Python will always be there to help you get the job done faster and more efficiently.
With this roadmap, you're now ready to embark on your journey to becoming a Python-powered ethical hacker. 🌐💻 Happy hacking! 👾
