Hacking Autonomous Vehicles: Ethical Pentesting for Smart Cars

Introduction: The Rise of Autonomous Vehicles
The rise of autonomous vehicles represents a revolutionary shift in transportation. With the potential to reduce human error, improve road safety, and transform urban mobility, these vehicles are no longer science fiction. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Cruise are at the forefront, testing and deploying self-driving cars across the globe.
However, this progress comes with significant cybersecurity challenges. Autonomous vehicles rely on complex systems, including artificial intelligence, real-time sensors, and wireless communications, which create multiple attack surfaces for malicious actors. A compromised vehicle can result in loss of control, data breaches, or even public safety hazards.
To ensure these smart cars are safe and resilient, ethical hackers conduct rigorous penetration testing. By identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, ethical hacking plays a crucial role in building secure autonomous vehicles and gaining public trust.
This article will explore the importance of ethical hacking, outline the attack surfaces, discuss common vulnerabilities, and provide insights into penetration testing techniques, tools, and legal considerations.
The Importance of Ethical Hacking for Smart Cars
Autonomous vehicles operate in a digital ecosystem that merges sensors, AI-driven algorithms, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. Each component introduces potential risks:
Unauthorized remote control of vehicles by hackers.
Sensor manipulation causing incorrect decision-making.
Data theft compromising privacy.
Real-world incidents highlight these risks. For example:
In 2015, researchers Charlie Miller and Chris Valasek remotely hacked a Jeep Cherokee, gaining control over its steering and braking systems.
Recent studies have demonstrated adversarial attacks on sensors, tricking LIDAR and camera systems into misinterpreting road conditions.
Ethical hacking provides a proactive defense by simulating cyberattacks under controlled environments. This allows vulnerabilities to be identified and addressed before malicious actors exploit them. With public trust and road safety on the line, ethical hacking ensures smart cars remain safe, reliable, and resilient.
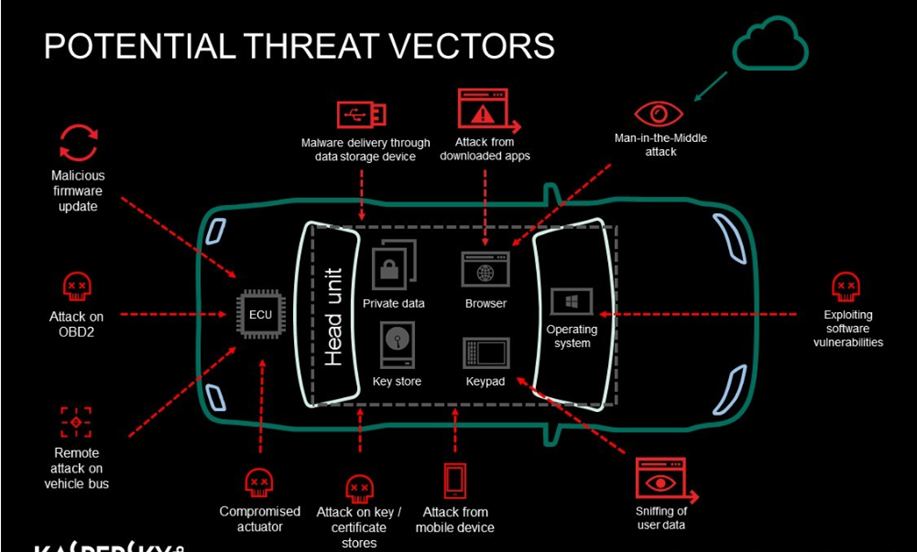
Mapping the Attack Surface of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles integrate diverse technologies, making them vulnerable across multiple attack surfaces:
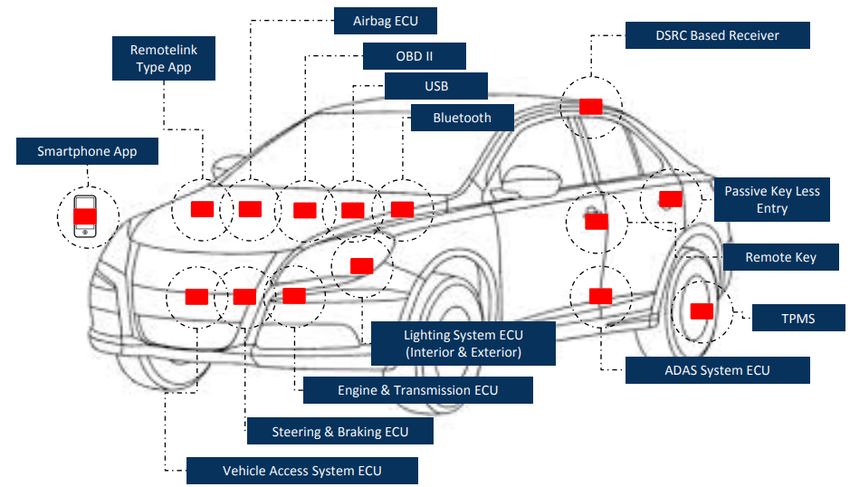
Hardware and Sensors
LIDAR, cameras, and radar gather critical environmental data. Hackers can manipulate these inputs with adversarial signals or obstruct detection to confuse the vehicle.
Communication Networks
Vehicles communicate using V2X protocols, such as Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) and Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I). Weak encryption or poor authentication can expose data to man-in-the-middle attacks or spoofing.
Autonomous Driving Software
The AI and machine learning models that control vehicle decisions may have software bugs or vulnerabilities, leading to unintended behavior.
APIs and Third-Party Integrations
Cloud services and third-party APIs enable features like software updates or remote access but can act as entry points for attackers if poorly secured.
By mapping these surfaces, ethical hackers can focus on securing the vehicle's entire digital ecosystem.
Common Vulnerabilities in Autonomous Vehicles
Some of the most common vulnerabilities in autonomous vehicles include:
GPS Spoofing
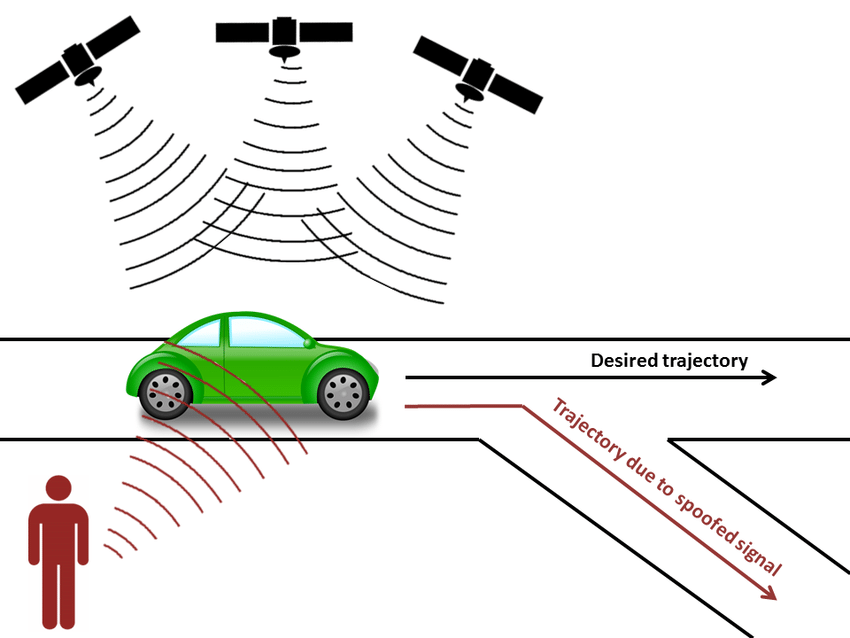
Hackers can broadcast fake GPS signals, misleading the car's navigation system to take incorrect routes.
Sensor Manipulation
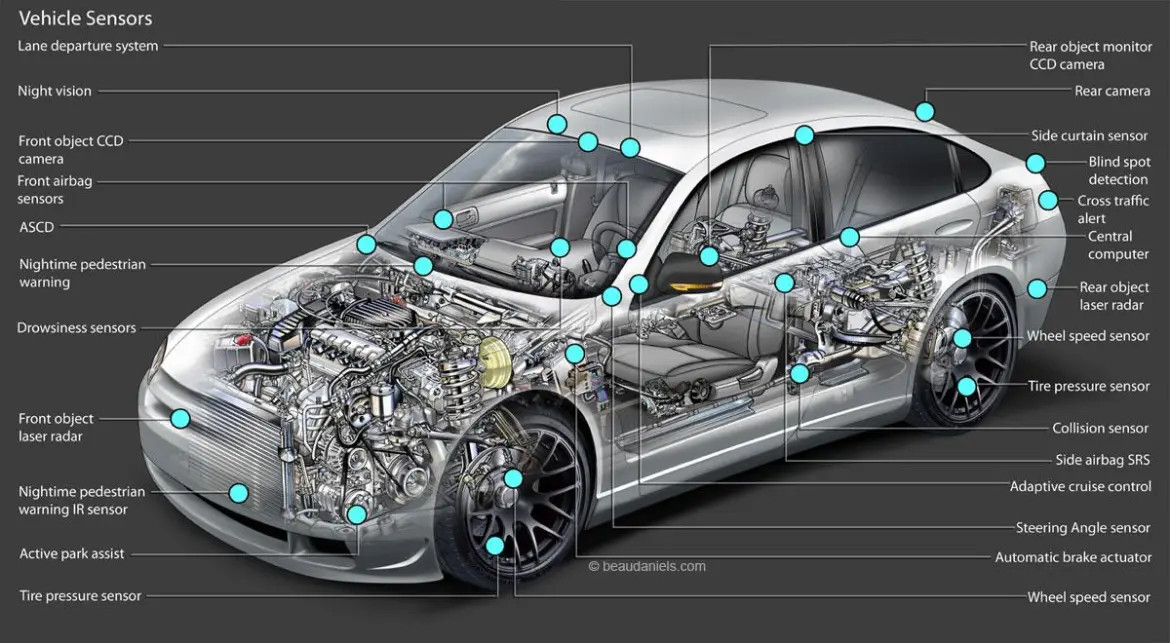
Adversarial inputs (e.g., misleading signals or visual interference) can deceive sensors like cameras and LIDAR.
Remote Control Exploits
Weaknesses in communication protocols or firmware allow attackers to remotely manipulate vehicle functions, such as acceleration, braking, and steering.
Data Exposure

Vehicles collect sensitive user data (e.g., location, driving habits), which can be leaked or stolen if systems lack strong encryption and security measures.
Understanding these vulnerabilities allows penetration testers to design effective testing strategies to mitigate risks.
Penetration Testing Techniques for Smart Cars
Ethical hackers use various techniques to test and secure autonomous vehicles:
Setting Up Testing Environments
Simulated environments, like CARLA and LGSVL, allow testers to experiment safely without using real vehicles.
Firmware Analysis and Reverse Engineering
Analyzing the vehicle's firmware for vulnerabilities helps identify weaknesses in low-level code.
CAN Bus Testing
The Controller Area Network (CAN bus) connects vehicle components. Ethical hackers test for weak encryption and inject malicious commands to identify exploits.
V2X Communication Validation
Testing for weaknesses in V2X protocols ensures secure data exchange between the vehicle and external systems.
By combining these techniques, testers can uncover and address security gaps effectively.
Essential Tools and Frameworks for Automotive Pentesting
Ethical hackers rely on specialized tools to perform penetration testing on smart cars. Key tools include:
CANoe and Wireshark for network analysis and CAN bus testing.
Scapy for crafting and testing packets in communication systems.
CARLA and LGSVL simulators for testing autonomous driving behavior.
JTAG and UART tools for hardware testing and debugging.
These tools empower testers to identify vulnerabilities in both software and hardware components.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Vehicle Hacking
While ethical hacking is vital, penetration testers must navigate legal and ethical boundaries to avoid violating laws. Key considerations include:
Adhering to GDPR and privacy laws when handling user data.
Following standards like ISO/SAE 21434, which outlines cybersecurity practices for automotive systems.
Reporting vulnerabilities responsibly to manufacturers and stakeholders to avoid legal repercussions.
Responsible disclosure ensures that findings contribute to improved security without jeopardizing trust.
Future Trends in Autonomous Vehicle Security
As technology evolves, so do the threats. Future trends in autonomous vehicle security include:

AI-Powered Security
Leveraging machine learning to predict and detect cyber threats in real time.
Evolving Communication Protocols
Enhancing V2X communication security through stronger encryption and authentication mechanisms.
Continuous Updates
Implementing over-the-air (OTA) updates to fix vulnerabilities promptly and keep vehicles secure.
The future will require collaboration between manufacturers, ethical hackers, and regulators to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Conclusion: Securing the Road Ahead
The development of autonomous vehicles marks a new era in transportation, but with innovation comes responsibility. Ethical hacking and penetration testing are essential to identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
By addressing attack surfaces, testing for vulnerabilities, and implementing advanced security techniques, ethical hackers ensure that autonomous vehicles are not only innovative but also safe and reliable. Public trust depends on cybersecurity, and ethical hackers play a crucial role in securing the future of smart mobility.
In this interconnected world, collaboration between manufacturers, hackers, and regulators will pave the way for a safer and more secure autonomous driving experience.
