AI for Cybersecurity: Enhancing Protection or Introducing New Risks?

As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool in the fight against digital attacks. From detecting anomalies to automating threat responses, AI-driven solutions promise to revolutionize cybersecurity defenses by spotting dangers at speeds and scales far beyond human capability. However, as much as AI has enhanced our ability to defend against cyber threats, it also presents unique challenges and risks. The very algorithms that protect us can be exploited, manipulated, or even misled, leaving networks vulnerable in new ways.
In this article, we'll explore the role of AI in cybersecurity, examining the technologies that power it, the benefits it offers, and the potential risks it introduces. By understanding both the power and limitations of AI, organizations can make better decisions about how to integrate this technology into their defenses without falling into the trap of over-reliance. Is AI a friend, foe, or perhaps a bit of both in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity? Let's dive in and find out.
1. The AI Revolution in Cybersecurity: Why It Matters Now More Than Ever
As technology advances, the sheer volume and complexity of cyber threats have skyrocketed, pushing traditional security measures to their limits. With attacks becoming more frequent, sophisticated, and damaging, AI-driven cybersecurity is proving invaluable for organizations aiming to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals. Unlike conventional software, AI systems can analyze vast datasets, recognize patterns of anomalous behavior, and even predict future risks—all at speeds far beyond human capability.
But why has AI become so essential? As attackers adopt increasingly advanced techniques, such as social engineering and multi-layered attacks, security teams require tools that are both highly adaptable and responsive. AI enables real-time responses to threats, allowing systems to adapt and defend almost instantaneously, something manual oversight alone could never achieve. In short, AI has transformed cybersecurity from a reactive measure into a proactive defense system capable of anticipating and neutralizing threats before they fully materialize.
In this section, we'll delve deeper into how AI's integration into cybersecurity began, why it's crucial in today's digital world, and the advantages it holds over traditional security approaches. Yet, as we'll explore further, this cutting-edge technology is not without its own unique challenges and potential pitfalls.
2. Understanding AI-Driven Cybersecurity: Key Technologies and How They Work
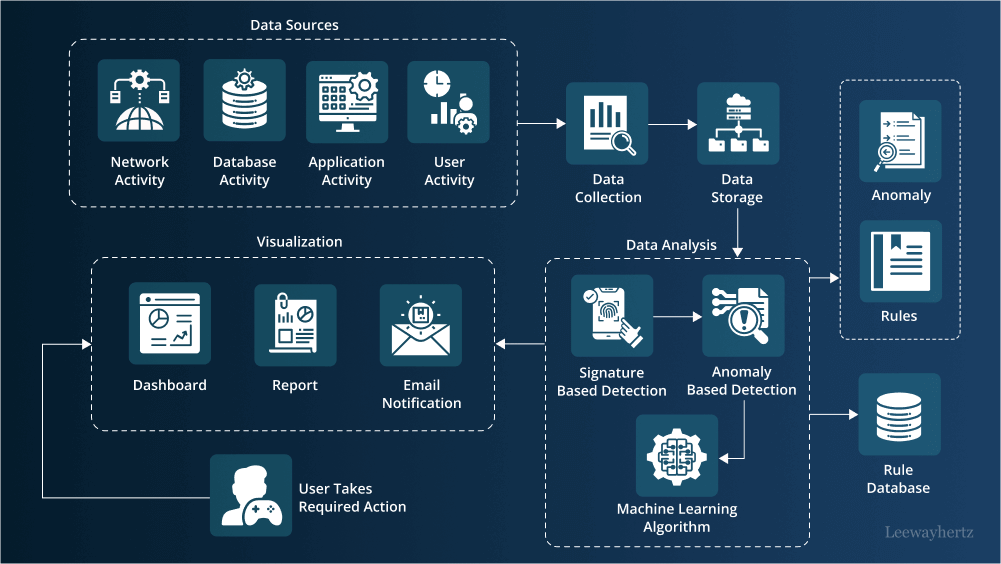
AI is not a single tool but rather a collection of cutting-edge technologies working in concert to detect and neutralize cyber threats. Each component—Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Neural Networks—plays a distinct role in identifying and preventing attacks.
Machine Learning (ML) allows systems to learn from vast amounts of data without being explicitly programmed. By analyzing previous attacks, ML algorithms can spot patterns and predict future threats. For example, machine learning models can detect anomalies that deviate from normal behavior, alerting security teams to possible intrusions in real time.
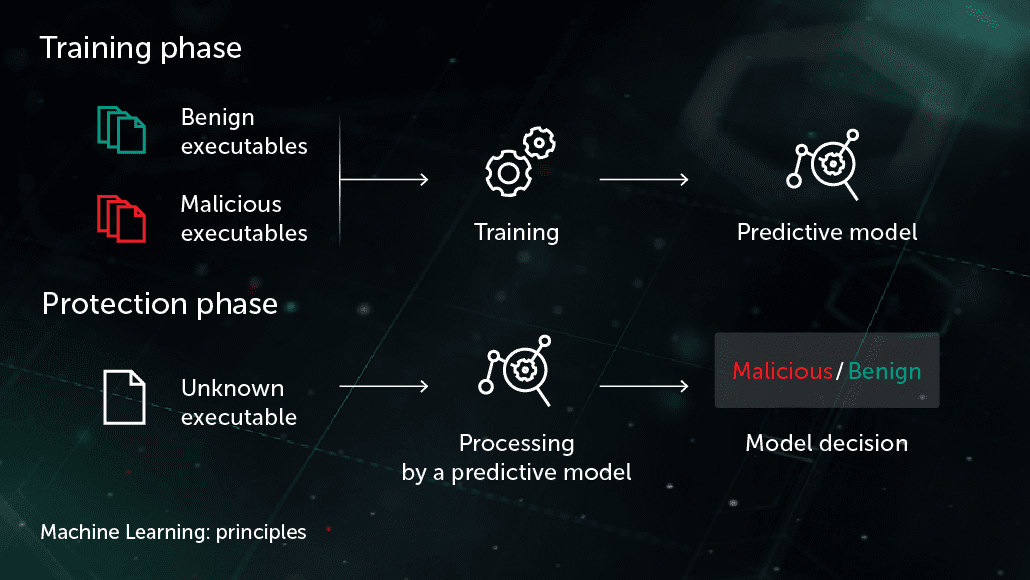
Deep Learning (DL) takes this a step further, using complex neural networks to process massive datasets and uncover subtle threats. While ML might identify that something unusual is happening, DL can analyze more granular details, helping to recognize threats that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Neural Networks are the backbone of both ML and DL, mirroring the human brain in their ability to process information across multiple layers. In cybersecurity, neural networks can process thousands of signals simultaneously, identifying threats at lightning speed.
These technologies collectively enable AI to adapt to evolving threats, constantly learning from new data and refining its understanding of what constitutes a security risk. However, while these tools bring powerful capabilities, they can also introduce blind spots and biases, which we'll discuss further in upcoming sections.
3. The Superpowers: What AI Brings to the Cybersecurity Table
AI has radically transformed the way cybersecurity works by providing capabilities that were once considered impossible. Some of the most significant superpowers AI offers include:
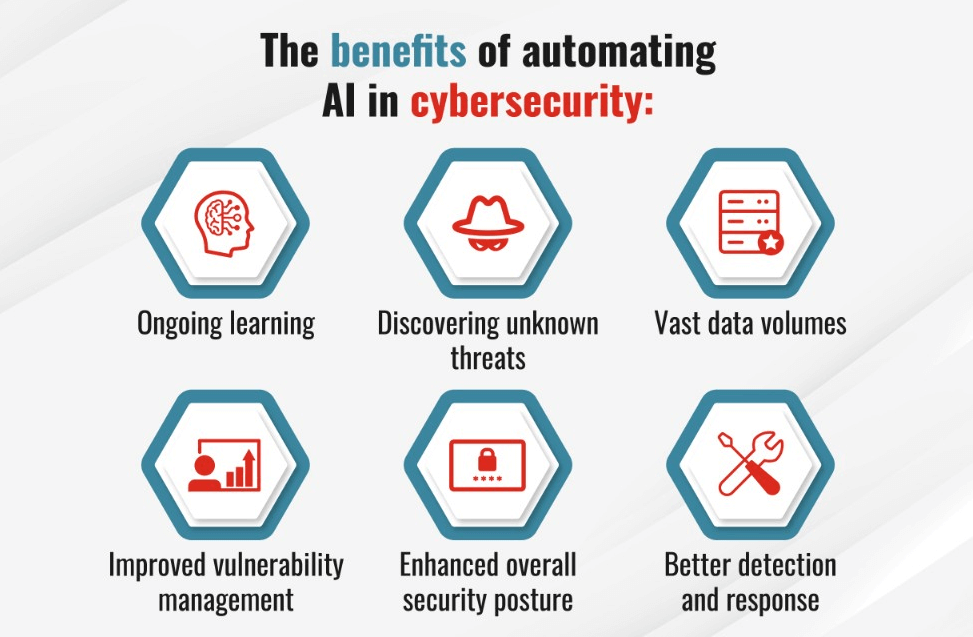
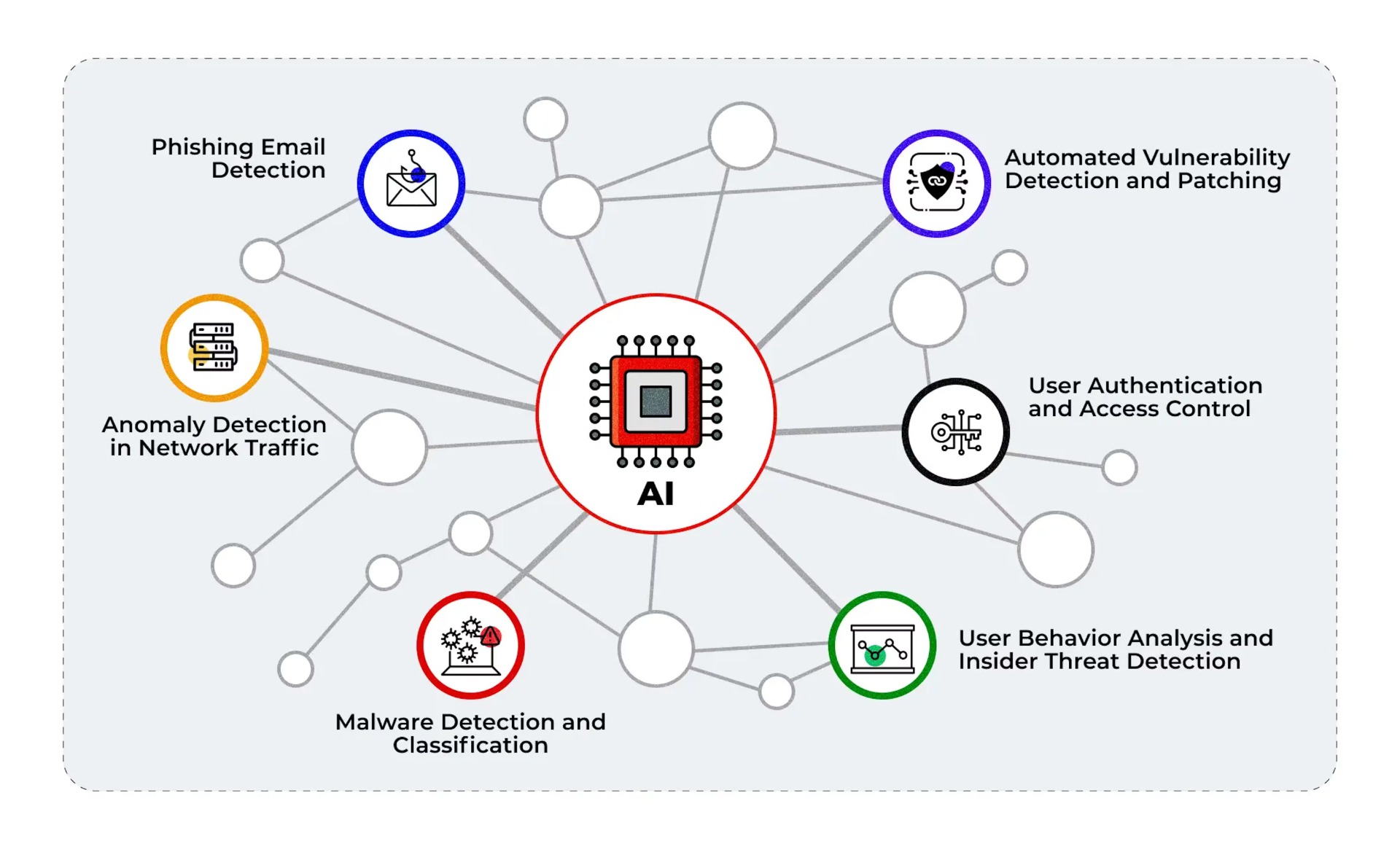
Anomaly Detection: Traditional security systems rely on a set of predefined rules to identify threats. However, AI uses anomaly detection to recognize deviations from normal behavior. This can include anything from unusual network traffic to a sudden spike in login attempts. Because AI can analyze vast amounts of data in real time, it's incredibly effective at spotting threats that may otherwise be overlooked. This proactive approach allows organizations to identify potential breaches before they cause serious harm.
Predictive Threat Intelligence: AI's ability to process and analyze historical data allows it to generate predictive insights about potential attacks. By studying past behavior, AI systems can forecast patterns and identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers. This gives businesses an edge by helping them strengthen their defenses before an attack even occurs. Predictive threat intelligence is a key advantage in a world where threats are evolving constantly.
Automation at Scale: One of the greatest benefits of AI in cybersecurity is its ability to automate responses to threats. Where manual intervention might take hours or days, AI can take immediate action. For example, if an attack is detected, AI can automatically block malicious traffic, isolate compromised systems, or even execute pre-defined countermeasures. This reduces response time significantly, limiting the potential damage from an attack and relieving the workload of cybersecurity professionals.
These superpowers help organizations manage the increasing volume of cyber threats more effectively and efficiently. But as AI becomes more integrated into cybersecurity, the question remains: Can it be fully trusted to handle such critical tasks on its own? We'll explore this and more as we continue.
4. The Flip Side: When AI Becomes a Double-Edged Sword
While AI has proven to be an invaluable tool for defending against cyber threats, it is not without its own vulnerabilities. Just as AI-driven systems can identify and block attacks, they can also be exploited by malicious actors to carry out new forms of cybercrime. This presents a significant challenge: the very technologies designed to protect us can, in the wrong hands, be turned against us.
AI-Powered Attacks: Hackers are increasingly using AI to develop more sophisticated attacks. For example, malware can be created that adapts in real time, learning how to evade detection by AI-powered defenses. This makes it more difficult for traditional security measures to keep up. The use of AI in creating deepfake videos or generating convincing phishing emails is another example of how cybercriminals leverage AI to deceive individuals and bypass security systems.
Exploitation of AI Systems: AI systems themselves are not immune to attack. Adversarial machine learning is an emerging field where attackers subtly manipulate data to deceive AI models. For example, by adding slight variations to an image, an attacker can trick an AI-powered facial recognition system into misidentifying a person. These types of attacks can render AI defenses ineffective, allowing attackers to bypass security measures without detection.
Over-Reliance on AI: One of the most dangerous risks is the growing dependence on AI for critical decision-making. If organizations place too much trust in automated systems without adequate human oversight, they may fail to detect subtle flaws or biases within AI algorithms. An over-reliance on AI could lead to false positives or false negatives, potentially causing serious security breaches or allowing attacks to slip through unnoticed.
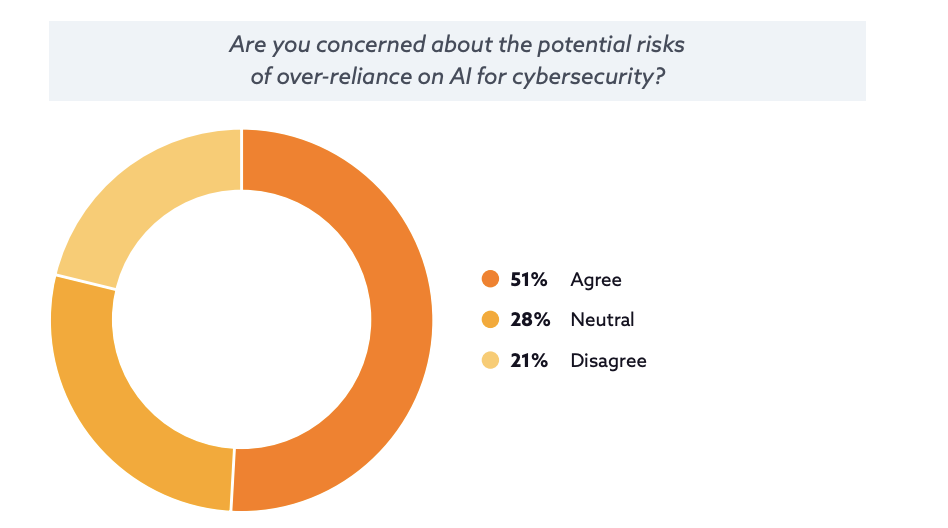
While AI offers incredible potential for enhancing cybersecurity, it also introduces a new set of risks that must be managed carefully. As we move forward, it's crucial to find a balance between the capabilities of AI and the necessity of human oversight to ensure that AI remains an asset, not a liability.
5. Adversarial Attacks: How Hackers Outsmart AI Systems
One of the most concerning risks associated with AI in cybersecurity is the rise of adversarial attacks—a new breed of cyberattack where hackers manipulate AI models to cause them to make errors. These attacks exploit the vulnerabilities in the algorithms that power AI systems, often in ways that are difficult to detect and prevent.
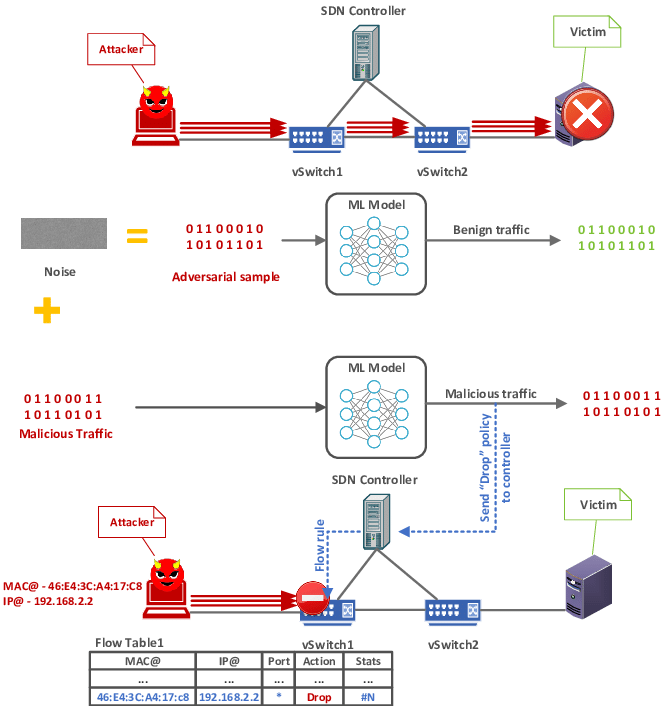
How Adversarial Attacks Work: In an adversarial attack, attackers introduce small, seemingly insignificant changes to input data, which then causes the AI system to misinterpret the information. For example, in image recognition systems, altering a few pixels in an image can trick the system into misclassifying an object, such as a stop sign being recognized as a yield sign. While these changes might be imperceptible to humans, they can have catastrophic effects on AI-powered security systems.
AI-Powered Malware: Hackers are also using adversarial techniques to create more stealthy malware that can bypass AI defenses. By understanding how AI systems detect malicious behavior, cybercriminals can craft malware that avoids detection by subtly altering its code. This makes it far more difficult for traditional security measures—and even AI defenses—to recognize and block the attack.
The Arms Race: As AI becomes a central part of cybersecurity, adversaries are constantly adapting and evolving their strategies to stay ahead. AI-powered defense systems must not only detect attacks but also anticipate them and adapt in real time. Defenders and attackers are engaged in a never-ending arms race, with each side using AI to gain an advantage over the other. This dynamic presents a constant challenge in maintaining the effectiveness of AI security systems.
Adversarial attacks represent a significant hurdle in fully trusting AI for cybersecurity, as even the most advanced systems can be deceived by clever manipulation. The key to countering this threat lies in creating more robust AI models that are resistant to adversarial inputs and integrating human oversight to catch what AI might miss.
6. AI Bias and Blind Spots: Are We Building a False Sense of Security?
As AI becomes more deeply integrated into cybersecurity systems, one of the most critical concerns is the potential for bias and blind spots within the AI models themselves. These issues can undermine the effectiveness of AI-powered defenses and even introduce new vulnerabilities.
Bias in AI Systems: AI algorithms learn from data, and if that data is biased, the AI model will reflect those biases. For example, if an AI is trained predominantly on data from a specific demographic or region, it may fail to recognize threats or behaviors that don't fit the patterns it has learned. This can lead to false positives (legitimate activities flagged as threats) or false negatives (threats that go undetected). In cybersecurity, such errors can have dire consequences, especially if they lead to missed attacks or unjustly block harmless activities.
Blind Spots in AI Security: AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on, and if the training data is incomplete or unrepresentative, blind spots can emerge. For example, a model trained to detect malware might perform well at recognizing known threats but may struggle to identify new, unknown types of malware. This lack of adaptability can allow cybercriminals to bypass AI defenses with novel tactics that haven't been incorporated into the training data yet. As a result, businesses could wrongly assume they are fully protected, when in reality, their systems are vulnerable to emerging threats.
The Need for Diverse Data Sets: One of the ways to combat AI bias and blind spots is through the use of diverse and representative data. By feeding AI systems a broad range of data—encompassing various attack vectors, demographics, and behaviors—organizations can create more accurate, fair, and adaptable models. However, gathering such data can be challenging, especially when trying to balance privacy concerns and regulatory requirements.
Although AI holds great promise in transforming cybersecurity, it's crucial to be aware of the limitations inherent in the systems. Relying too heavily on AI without considering these potential weaknesses could lead to a false sense of security. Understanding and mitigating AI's blind spots and biases is vital to ensuring the technology enhances cybersecurity rather than undermining it.
7. The Human Factor: Why AI Needs a Human Touch in Cybersecurity
Despite the impressive capabilities of AI, it's essential to recognize that AI systems are not infallible and cannot replace human expertise entirely. Cybersecurity professionals play an indispensable role in complementing AI-driven defenses, ensuring that AI tools remain accurate, ethical, and aligned with the broader security strategy.

AI as a Tool, Not a Replacement: While AI can handle the bulk of repetitive tasks, such as scanning for malware or analyzing traffic patterns, it is still heavily reliant on human oversight. Humans bring creativity, intuition, and context that AI systems lack. For instance, AI might flag a piece of software as malicious based on patterns, but it's a skilled cybersecurity expert who can assess whether the software is part of an authorized tool or a legitimate update. Human intervention ensures that AI systems operate within the correct context, reducing the risk of false alarms and ensuring more accurate results.
AI Cannot Understand the Bigger Picture: AI excels in processing large amounts of data, but it cannot understand the broader, evolving nature of the threat landscape. Cybersecurity experts are needed to interpret the patterns AI detects and make strategic decisions about how to respond. Threat intelligence, for example, requires not just analyzing data, but understanding the motivations behind attacks, the potential targets, and the possible long-term impacts—all areas where humans still outperform AI.
Collaboration Between AI and Humans: The most effective cybersecurity strategy integrates both AI and human intelligence. AI can automate routine tasks and perform complex analyses at scale, while cybersecurity professionals can focus on high-level decision-making and strategy. By combining the speed and efficiency of AI with the judgment and experience of human experts, organizations can achieve a more resilient and adaptive defense system.
While AI enhances the efficiency of cybersecurity systems, the human touch is still necessary to ensure that decisions are made with context, ethical consideration, and strategic foresight. It's a powerful partnership that strengthens defenses without over-relying on automation alone.
8. AI in Cybersecurity: Balancing Innovation with Ethical Responsibility
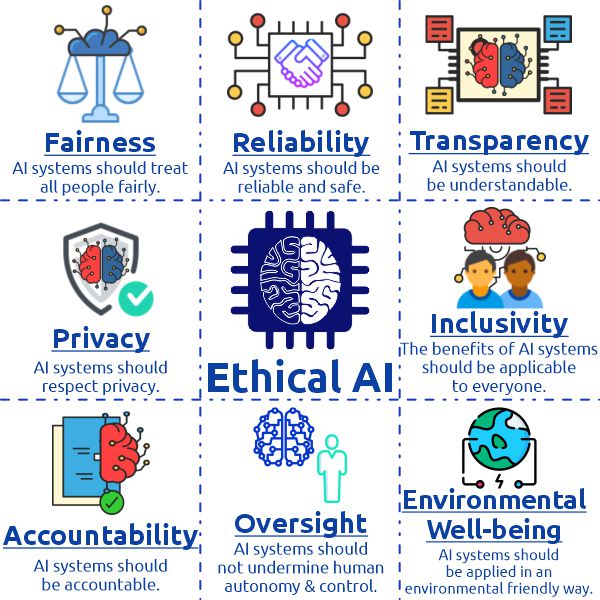
As AI continues to shape the future of cybersecurity, it's crucial to address the ethical implications of its deployment. The integration of AI into critical security systems raises questions about privacy, fairness, transparency, and accountability. While AI offers innovative solutions, it's essential that these systems are developed and used in a responsible manner to avoid unintended consequences.
Privacy Concerns: AI systems often require access to large datasets to function effectively, which may include sensitive personal information. This raises significant concerns about privacy. For example, AI-driven tools used for anomaly detection may inadvertently monitor user activity in ways that violate individual privacy rights. Organizations must ensure that AI systems are designed to protect user privacy, using encryption, data anonymization, and other safeguards to mitigate risks.

Bias and Fairness: As discussed earlier, AI algorithms can inherit biases from the data they are trained on. When AI systems are used to make critical decisions—such as blocking access to sensitive information or determining whether an employee's actions are suspicious—it is essential that these decisions are made fairly. Ethical AI development involves ensuring that algorithms are transparent, auditable, and free from discriminatory practices. It's crucial that organizations prioritize fairness when deploying AI in cybersecurity.

Accountability: As AI systems take on more decision-making power, the question of accountability becomes increasingly important. Who is responsible if an AI-driven system fails to detect an attack, or worse, causes a security breach? In some cases, the lack of transparency in AI decision-making can make it difficult to determine the cause of an error. It's vital that businesses have clear accountability structures in place, ensuring that human experts remain in charge and can intervene when necessary.

The Need for Ethical Guidelines: As AI continues to evolve, it's imperative that organizations, regulators, and researchers collaborate to create ethical guidelines for the use of AI in cybersecurity. These guidelines should address issues such as data privacy, transparency, algorithmic fairness, and the responsibility of AI developers. By establishing ethical standards, we can ensure that AI is used for the benefit of society while minimizing the potential harms.
As the use of AI in cybersecurity grows, it's essential to balance the pursuit of technological innovation with ethical responsibility. Without careful consideration of the broader implications, AI systems could inadvertently introduce new risks, undermining the very security they were designed to protect.
9. The Future of AI in Cybersecurity: What Lies Ahead?
Looking ahead, the role of AI in cybersecurity will only continue to expand. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, AI will play an even more pivotal role in defending against malicious activities. But as we embrace AI-driven security solutions, we must also consider the evolving landscape of challenges and opportunities it presents.
AI and Quantum Computing: One of the most exciting prospects for AI in cybersecurity is its intersection with quantum computing. Quantum computers promise to revolutionize the way we process and encrypt data, offering immense computational power. This could help AI systems solve complex security problems faster and more efficiently. However, quantum computing also poses a potential risk to current encryption methods, which may be vulnerable to quantum-based attacks. The combination of AI and quantum computing could lead to groundbreaking advancements in both cybersecurity defenses and offensive strategies.
AI-Powered Automation and Response: In the near future, we can expect AI to take on even more responsibility in automated threat response. As AI systems become more advanced, they will not only detect and predict threats but also take immediate action without human intervention. This could include automatically neutralizing malware, isolating compromised systems, and executing patches to vulnerabilities, all in real-time. As automation in cybersecurity grows, organizations will need to ensure that their AI systems are both secure and ethically responsible to prevent unintended consequences.
Human-AI Collaboration Will Continue: Despite the many advancements in AI, the role of human expertise will remain essential in cybersecurity. Rather than replacing human professionals, AI will work alongside them, enhancing their ability to defend against attacks and analyze complex situations. Collaboration between human intuition and AI's processing power will be crucial in staying ahead of cybercriminals, providing a multilayered defense that combines the strengths of both.
Ethical AI and Governance: As AI becomes more embedded in cybersecurity, the focus on ethics, transparency, and regulation will only intensify. Future developments will likely include stricter regulations around the use of AI in security applications, as well as clearer frameworks for accountability. Governments, industries, and researchers will need to work together to create governance models that ensure AI is used responsibly and ethically across the cybersecurity landscape.
The future of AI in cybersecurity is bright, but it is not without its challenges. By addressing the risks, embracing the potential of new technologies, and maintaining a strong focus on ethical responsibility, we can harness the power of AI to create a more secure digital world.
10. Conclusion: Embracing AI with Caution and Vigilance

AI has unquestionably transformed the landscape of cybersecurity, offering unprecedented capabilities in threat detection, prevention, and response. As organizations continue to adopt AI-driven systems, the benefits are clear: faster response times, the ability to handle vast amounts of data, and enhanced accuracy in identifying and mitigating risks. However, as we've explored, these powerful tools also come with their own set of challenges.
From adversarial attacks and AI bias to the need for human oversight and ethical responsibility, the integration of AI into cybersecurity requires a careful, measured approach. The key to success lies not in fully automating defense systems or placing blind trust in AI, but in creating a collaborative environment where AI works alongside human expertise. In this way, AI can be a force multiplier, enhancing cybersecurity efforts without replacing the nuanced judgment of skilled professionals.
As we move forward, organizations must embrace innovation while remaining vigilant about the risks and responsibilities associated with AI. By continuing to refine AI technologies, address ethical concerns, and invest in human talent, businesses can create more robust defenses against the increasingly complex cyber threats of tomorrow.
The future of cybersecurity will undoubtedly be shaped by AI, but the balance between its power and its pitfalls will determine how well we are able to protect our digital lives.
